Cervical cancer was one of the diseases that cost the most lives in the United States many years ago. The excellent news is that based on a study reported by the Centers for disease, control, and prevention (CDC), deaths caused by cervical cancer have declined significantly in the last 40 years, and this is due to a culture of prevention. Recently women are becoming more aware and taking control of their health. This decline largely is the result of many women getting regular Pap tests, which can find cervical pre-cancer cells even before it turns into cancer. Are you ready? Let’s begin!
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that develops when the cells of the uterine cervix become cancerous.
The most common cause of cervical cancer.
The number 1 cause of cervical cancer is infection with human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted disease.
When there is an exposure to HPV, the immune system attacks it, preventing further damage to the cervix cells. But sometimes the virus can survive and remain dormant in the cervix for years, causing a chronic inflammatory process, which causes the cervix cells to mutate and become cancer cells.
The causes of why cervical cancer occurs are not very clear, but it is known that HPV plays a fundamental role in the development of the disease. While some women with HPV never develop the disease, there are others who do develop it, this is because there is also a relationship with other factors such as environment and lifestyle.
Symptoms of cervical cancer.
In the early stages, cervical cancer usually does not show any symptoms, this is precisely the reason why having annual exams and regular PAP smears can make the difference.
In the late stages of cervical cancer, this is the signs and symptoms.
- Pelvic pain.
- Pain or abnormal bleeding during or after sexual intercourse.
- Unusual vaginal discharge.
- Abnormal bleedings in the middle of the cycle.
- Postmenopausal abnormal bleeding.
Types of cervical cancer.
The fundamental types of cervical cancer are
- Squamous cell carcinoma: This is the most common and begins in the thin and flat cells of the cervix called squamous cells, these cells are responsible for covering the outside of the cervix.
- Adenocarcinoma: This type of cervical cancer begins in the column-shaped glandular cells that line the cervical canal.
- Adenosquamous carcinoma: The rarest form of cervical cancer. In some patients, the 2 types of cells are involved in cervical cancer.
Very rarely cervical cancer develops in other cervix cells that are not mentioned above.
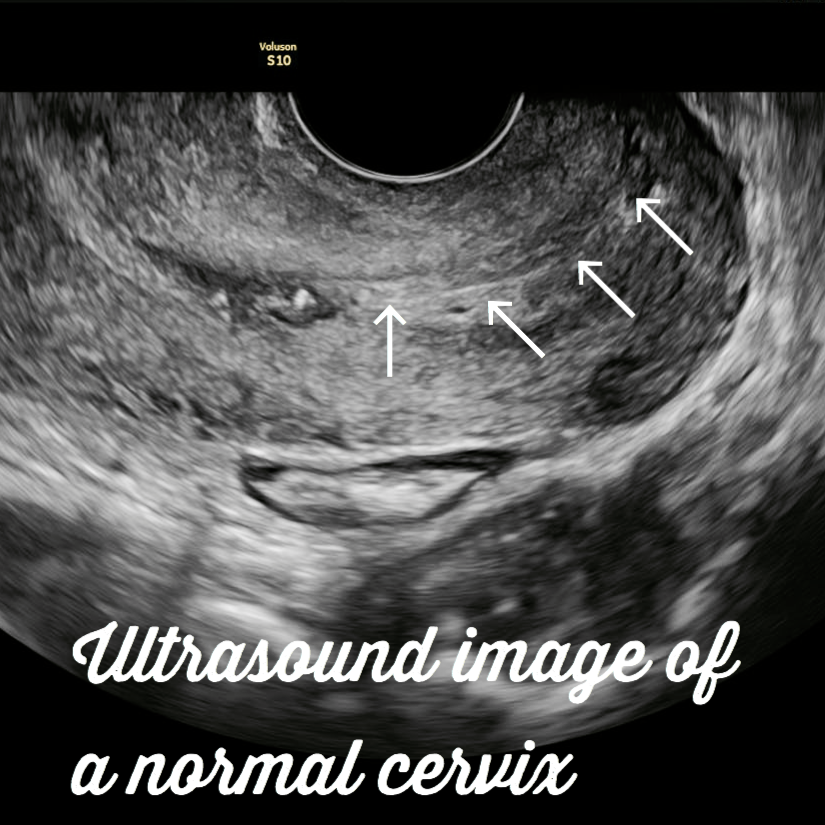
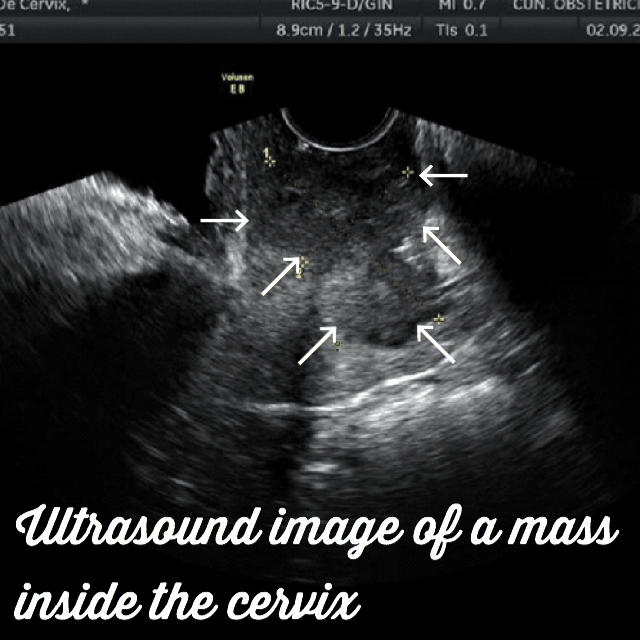
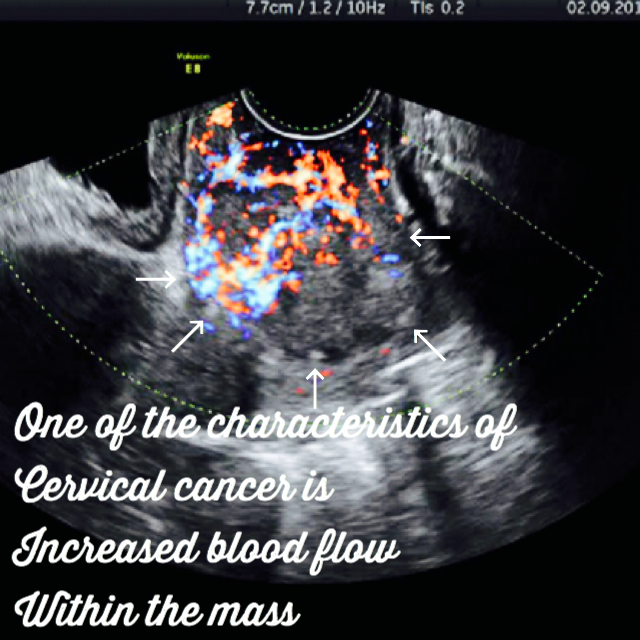
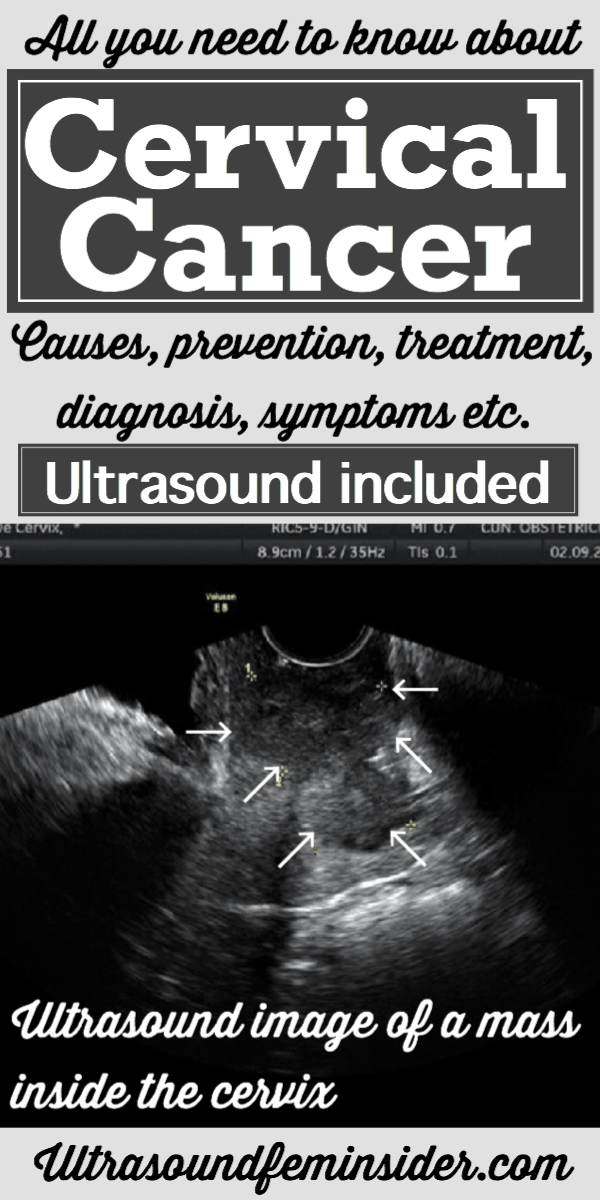
Diagnosing cervical cancer. Ultrasound images.
Related post you might like to read after!
Irregular periods. Causes, treatment, natural remedies, ultrasound and more.
Endometrial ablation, all you need to know.
Pelvic pain in women. Role of ultrasound diagnosing pelvic pain.
Ovaries, hormonal cycles, and common cysts.
Uterine Fibroids, how to naturally treat and prevent them.
Risk factors for cervical cancer:
- Many sexual partners: The greater the number of sexual partners you have, the greater the risk of contracting the disease. It should be noted that on many occasions men do not have symptoms, and do not even know that they are infected.
- Early sexual activity: The younger the sexual relations begin, the greater the risk of developing the disease.
- Previous exposure to other sexually transmitted diseases: having been infected with other sexually transmitted diseases may increase the risk. Diseases such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis or HIV / AIDS increase the risk.
- A weak immune system: Your immune system is the number one barrier that attacks the virus and protects you in case of exposure to the virus. If your immune system is weak, and the virus survives in the cervix, the probability of suffering from the disease increases dramatically.
- Smoking: The habit of smoking is associated with the development of squamous cell cervical cancer.
- Exposure to D.E.S: Diethylstilbestrol or (D.E.S) was a drug that was used for miscarriage prevention in the 1950s if your mother took this drug you could be at greater risk of developing adenocarcinoma.
- The use of Oral contraceptives for extremely long periods of time.
How to prevent cervical cancer.
- Find out about the HPV vaccine: The HPV vaccine inoculates the sleeping HVP virus inside your body, so your immune system will create the corresponding antibodies to attack it if one day you are exposed to the virus. Therefore, Inform yourself and ask your doctor if the HPV vaccine is appropriate for you. The HPV vaccine is not only applied to girls but also to boys to protect them from infections.
- Keep up with your regular checkups and PAPs: PAP smear consists of extracting tissue from the cervix and sending it to the laboratory. The PAP throws important information about the health of your cervix, among that information includes if you have HPV and if there are pre-cancerous cells in the cervix.
- Practice safe sex and make sure your partner does the same: Practicing safe sex with only one partner will drastically decrease your chances of getting HPV and developing cervical cancer. Including on practicing safe sex, there is also the use of condoms to protect yourself from unnecessary exposure.
- Avoid smoking: The habit of smoking is one of the worst, not only have cancer risks in the larynx, lungs, oral area, etc. But it also affects the cervix cells. Take care of yourself, avoiding smoking.
Share the post here!
Treatment.
Among the treatments for cervical cancer are surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. Regardless of the fact that mortality cases have decreased dramatically in the last 40 years, it should be noted that cervical cancer is still another cause of death, and must be treated appropriately by a health professional.
There are also very effective treatments for patients with HPV and changes with pre-cancerous cells. These treatments will prevent these pre-cancerous cells to become cancerous.
Among these treatments are
- Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP). A thin, electrically charged wire is used to remove abnormal lesions from your cervix.
- Freezing (cryotherapy). Some pre-cancerous cervical lesions can be destroyed by freezing them with a cold probe.
- Laser treatment. The precancerous cervical lesion is destroyed with a beam of laser light.
- Conization. A small, cone-shaped piece of tissue containing the abnormal area of the cervix is removed surgically.
Final thoughts.
As you can see cervical cancer can be dangerous. But this days, there is a well-established culture of prevention among women and men, starting from adolescence with the HPV vaccine. Therefore, there is a way to protect ourselves and teach our children to protect themselves as well. This measures combined with the adoption of healthy habits, such as: the use of condoms, and the practice of safe sex, are just some of the few things you can do to avoid unnecessary exposure and infection.
On the other hand, treatments today are quite effective in curing cervical cancer once it has developed. The key is in the prevention and early detection with regular exams.
I hope this article was helpful and informative to you. If so, share it with other women who might need this information.
Zadi, xo
Disclaimer: This post is not intended to diagnose, treat, prevent, or cure any disease. For proper medical attention, please visit your physician.










excellent submit, very informative. I ponder why the opposite specialists of this sector do not realize this. You should continue your writing. I am confident, you’ve a huge readers’ base already!
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I have joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I have shared your site in my social networks!