When you’re pregnant, the last thing you want or hope to hear is that something is wrong with your baby. Spina bifida is a birth defect where the baby’s spine does not form properly. Spina bifida is a neural tube defect. The neural tube is the structure in a developing embryo that eventually becomes the baby’s brain, spinal cord, and the tissues that enclose them. In this article, I am going to give you the most essential information related to spina bifida, you will also find ultrasound photos associated with the diagnosis of spina bifida. Ready? Let’s get started.
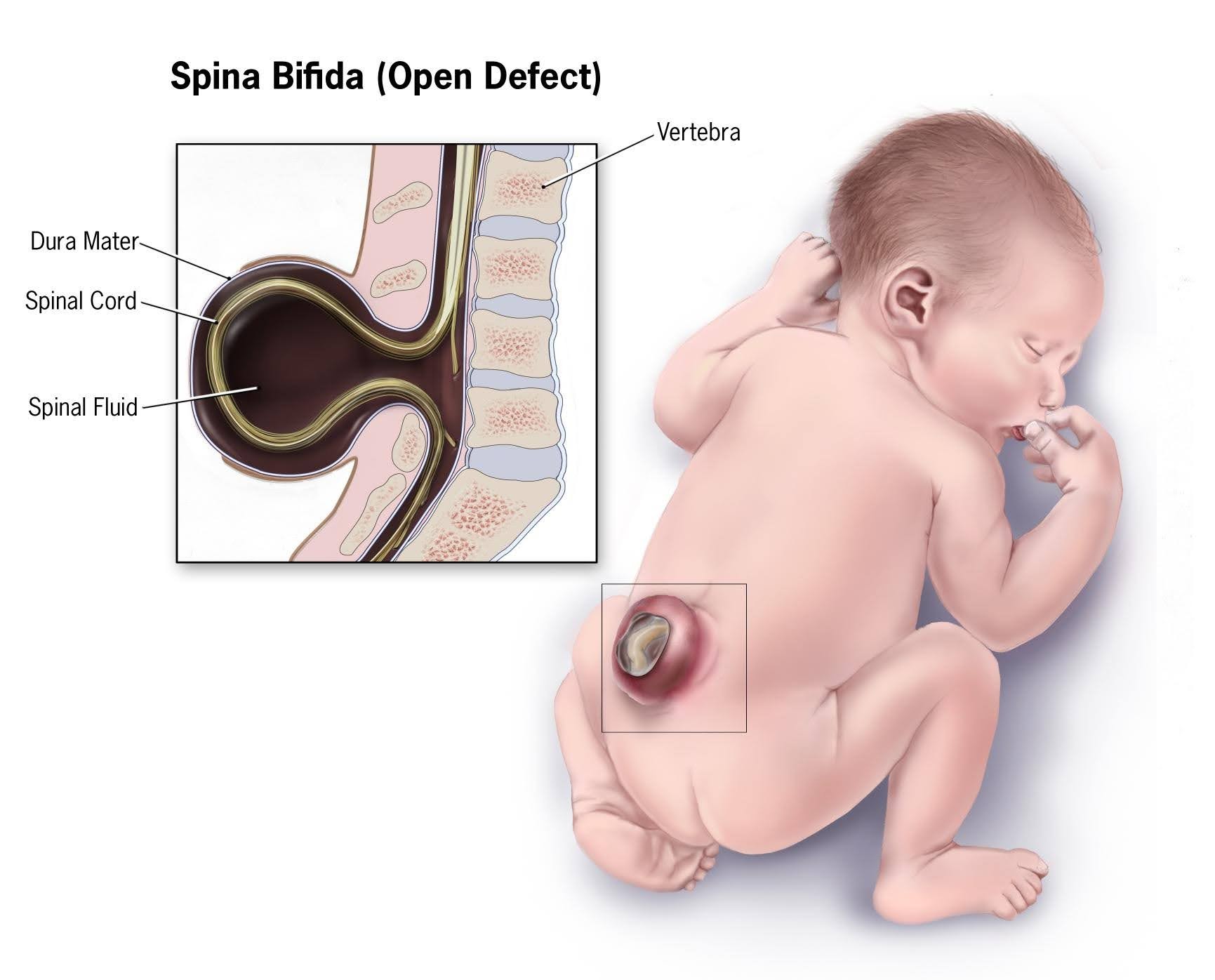
What is precisely spina bifida.
The nervous system develops from a small, specialized plate of cells along the back of an embryo called the neural plate, early in development. The edges of this plate begin to curl up toward each other, creating the neural tube, a narrow sheath that closes to form the brain and spinal cord of the embryo. As development progresses, the top of the tube becomes the brain, and the remaining lower portion becomes the spinal cord.
This process is usually completed by the 28th day of pregnancy after conception. If a problem occurs during this process, the result can be neural tube defects, including spina bifida.
Spina bifida causes.
The causes of spina bifida are not clearly understood by science. However, it is believed that it may be a combination of different reasons, such as genetic disorders, nutritional deficiencies, and environmental factors.
Spina bifida can range from mild to severe depending on size and location. Therefore each case is carefully studied, and the treatment will depend on the severity of the spina bifida.
Types of spina bifida with their symptoms.
There are different types of spina bifida, and I am going to explain all of them below.
Spina bifida occulta
This type of spina bifida is the mildest and most common type, “occulta” means hidden. Spina bifida occulta occurs when there is a small separation or gap in one or more of the bones of the spine (vertebrae). Many people who have spina bifida occulta don’t even know it, unless the condition is discovered during an imaging test done for unrelated reasons. This type of spina bifida might have or might not have symptoms ever in their lives. Therefore in the majority of the cases are found accidentally.
Meningocele
Spinal fluid and meninges protrude through an abnormal vertebral opening. This malformation contains no neural elements and may or may not be covered by a layer of skin. Some individuals with meningocele may have few or no symptoms, while others may experience such symptoms as complete paralysis with bladder and bowel dysfunction.
Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele is the most severe type. In myelomeningocele, the spinal cord/neural tissues are exposed through the opening in the spine, resulting in partial or complete paralysis of the parts of the body below the spinal opening. The impairment may be so severe that the affected individual is unable to walk and may have bladder and bowel dysfunction.
To visit our YouTube channel, click here.
Risks factors of spina bifida.
Although the origin of why spina bifida occurs is not very clear today, if some risk factors have been identified.
- If you have a personal or family history of spina bifida: The chances of having a baby with this condition are higher. This means that If you were born with spina bifida, or if your husband was born with spina bifida, the chance of having a baby with spina bifida is higher, this could be related to genetic problems. Or if there are other people with the condition in the family history as well.
- Specific ethnicity: It has been identified that cases of spina bifida are higher among the white or Hispanic population.
- Baby Gender: The percentage of cases of spina bifida is higher among female babies compared to boys.
- Diabetes mellitus: Women with diabetes mellitus who don’t have well-controlled blood sugar levels have a higher risk of having a baby with spina bifida.
- Folate deficiency: Folate, the natural form of vitamin B-9, is essential to the development of a healthy baby. The synthetic form, found in supplements and fortified foods, is called folic acid. A folate deficiency increases the risk of spina bifida and other neural tube defects in babies. That is why it’s so important to take vitamins before and during pregnancy, but especially in the first trimester, which is the time when the spine is forming to avoid this risk.
- Certain medications: Anti-seizure medications, such as valproic acid (Depakene), seem to cause neural tube defects when taken during pregnancy. This might happen because they interfere with the body’s ability to use folate and folic acid.
- Obesity: Pre-pregnancy obesity is associated with an increased risk of neural tube birth defects, including spina bifida.
Sharing is caring!!
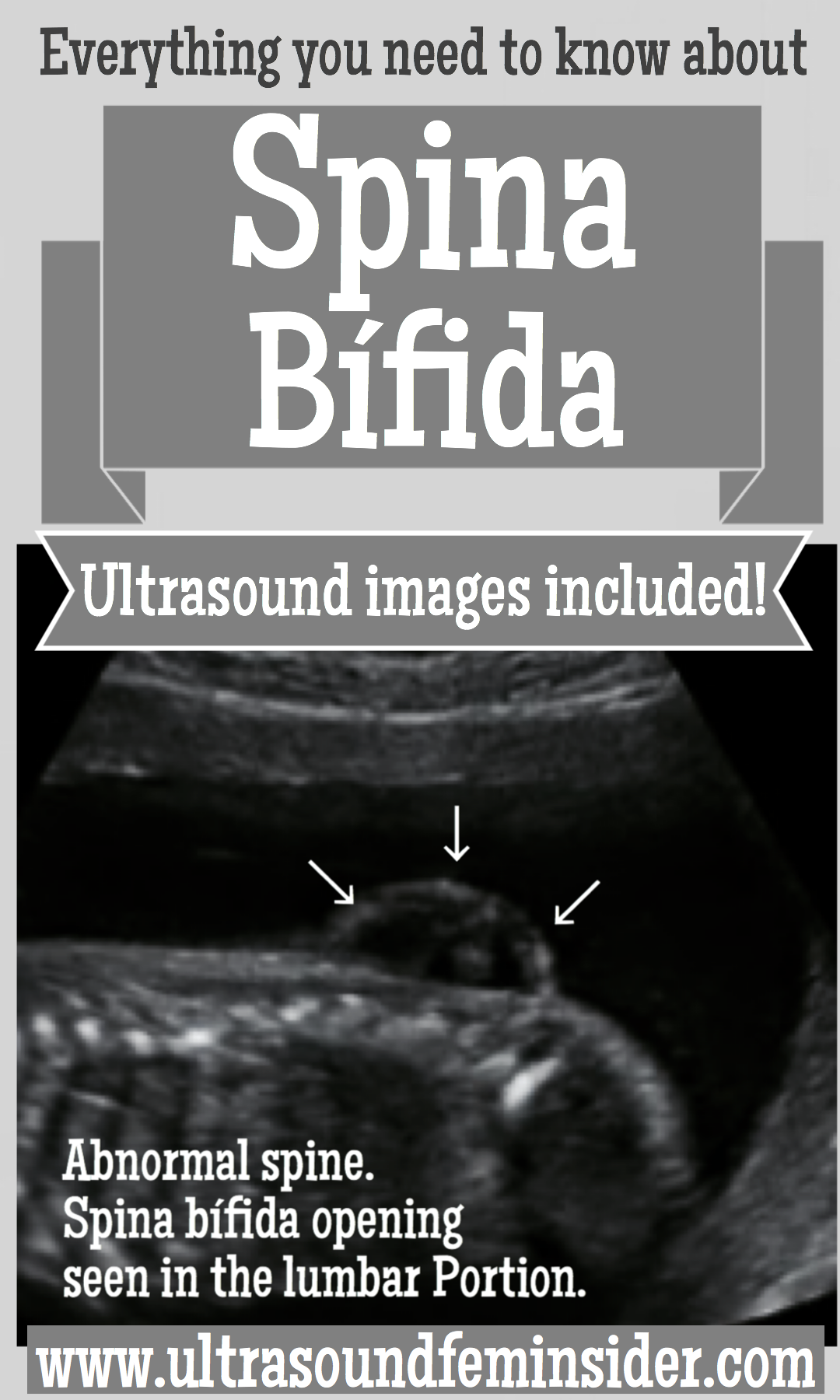
Diagnosis of spina bifida.
The most common screening methods used to look for spina bifida during pregnancy are second-trimester maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening and fetal ultrasound.
The maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein or MSAFP screen is done at 16-18 weeks of gestation. It measures the level of a protein called alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), which is naturally formed by the fetus and the placenta. During pregnancy, a small amount of AFP regularly crosses the placenta and enters the mother’s bloodstream. If abnormally high levels of this protein appear in the mother’s blood, it may be an indication that the fetus has a neural tube defect. The MSAFP test, however, is not specific for spina bifida and requires correct gestational dates to be most accurate; it cannot definitively determine that there is a problem with the fetus. If a high level of AFP is detected, the doctor may request additional testing, such as an ultrasound or amniocentesis, to help determine the cause.
The second-trimester MSAFP screen described above may be performed alone or as part of a larger, multiple-marker screen. Multiple-marker screens look not only for neural tube defects, but also for other congenital disabilities, including Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities. First trimester screens for chromosomal abnormalities also exist, but signs of spina bifida are not evident until the second trimester when the MSAFP screening is performed.
Amniocentesis is an exam in which the doctor removes samples of fluid from the amniotic sac that surrounds the fetus may also be used to diagnose spina bifida. Although amniocentesis cannot reveal the severity of spina bifida, finding high levels of AFP and other proteins may indicate that the disorder is present.
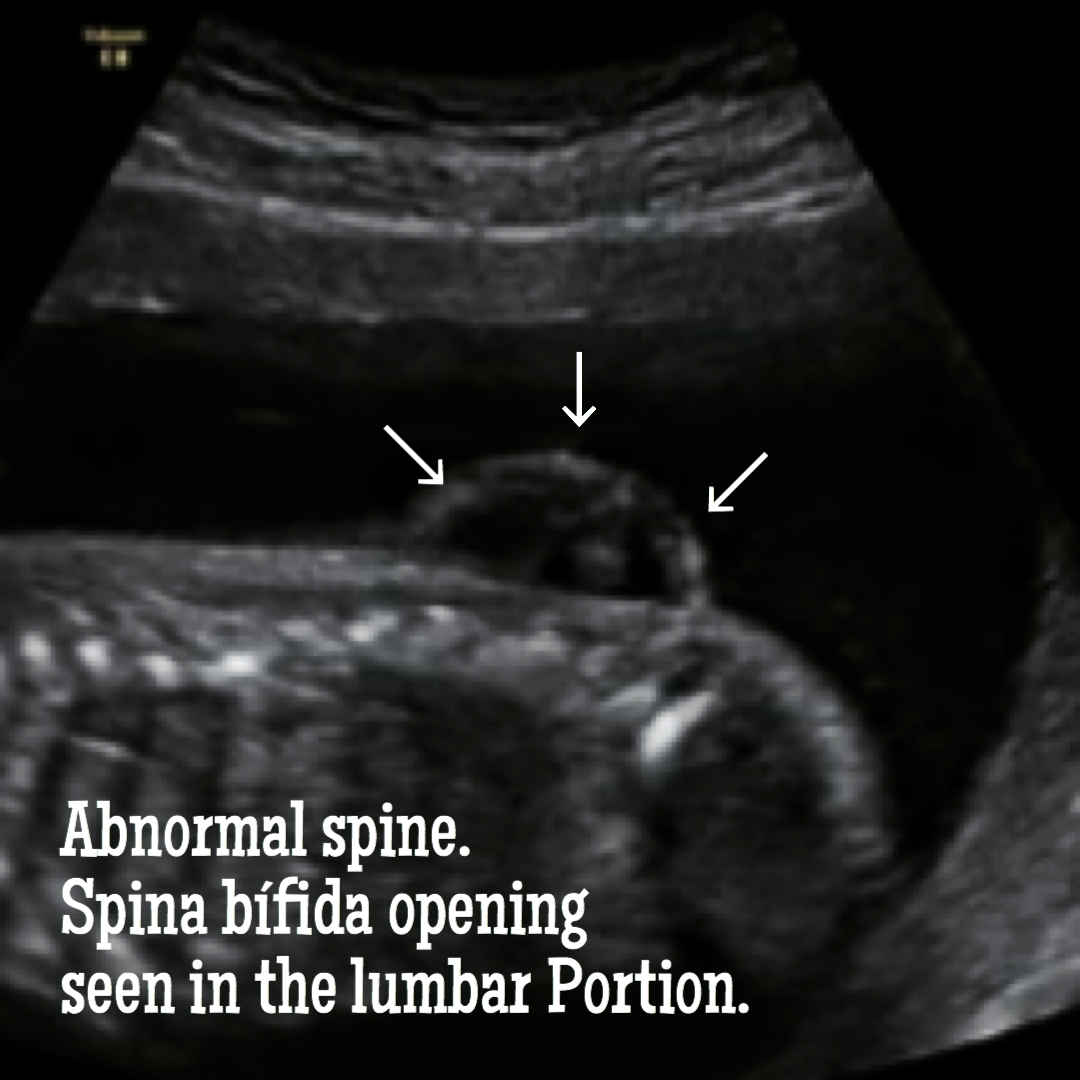
How spina bifida is seen and confirmed with ultrasound.
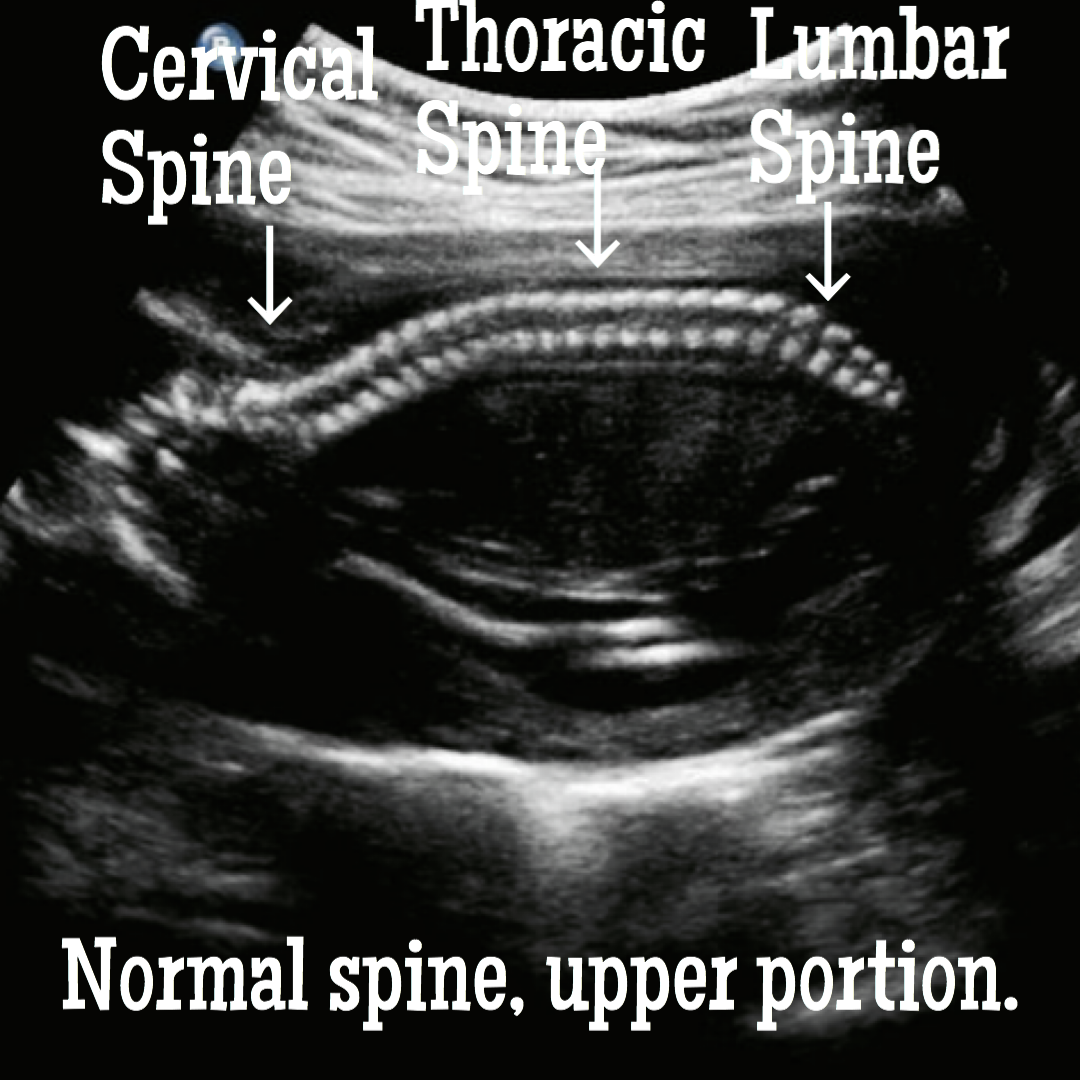
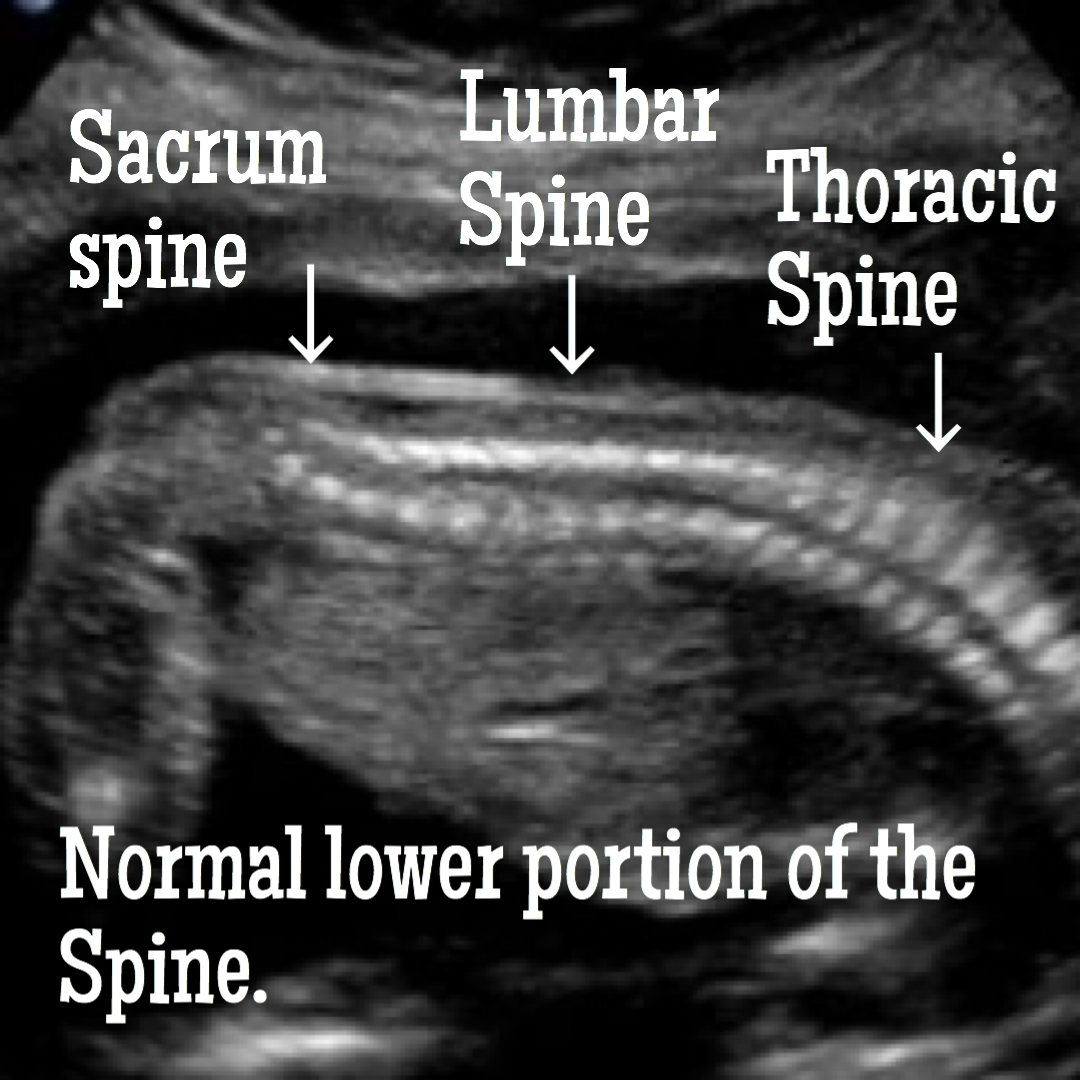
Is it possible to prevent spina bifida?
Not entirely, although there are things you can do to lower your risk.
- If you were born with the condition, or your husband, or the condition exists in the family, the most advisable thing is to consult with your doctor to know your options, and to receive more thorough exams.
- Maintaining a healthy weight before getting pregnant, a balanced and healthy diet, in addition to an exercise routine can help you.
- Before you conceive, start taking prenatal vitamins to supply nutritional deficiencies in your body before you get pregnant. The recommendation for women trying to get pregnant is to take a daily supplement of 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid.
- If you are trying to get pregnant in addition to the vitamins, you can increase the consumption of foods rich in folate such as Pasta, some breakfast cereals, rice, and enriched breads.
- If you have pre-existing conditions, consult with your doctor, and in the case of diabetes, it is essential to have sugar levels under control.
Spina bifida occulta does not cause any complications. On the other hand, severe, open spina bifida or myelomeningocele, if it can cause many complications.
Here is a list of these complications.
Walking problems: The nerves from the spine that control the muscles on the leg don’t work correctly below the area of the spina bifida defect. This can cause muscle weakness of the legs and sometimes paralysis.
Orthopedic complications: Babies born with myelomeningocele can develop a variety of problems in the legs and spine because of muscle weakness in the legs and portions of the back. The types of problems depend on the location of the defect. This orthopedic problems might include: Curved spine (scoliosis), Muscle contractures, Dislocation of the hip, bone and joint deformities.
Bowel and bladder problems: The nerves that supply the pelvic cavity, urinary bladder, and lower intestines generally do not function properly when children are born with myelomeningocele. This is because the nerves that supply the bowel and bladder come from the lowest level of the spinal cord, the possible location of the defect.
Abnormal buildup of fluid in the brain, also known as hydrocephalus: Babies born with myelomeningocele, usually experience fluid buildup in the brain.
Infection in the tissues that surround the brain or meningitis: Meningitis is an infection in the tissues that surround the brain, it occurs due to the exposure of the tissue in the defect of spina bifida. This is a life-threatening condition that, if not treated quickly, can cause irreversible brain injury.
Sleep-disordered breathing or sleep apnea: Both children and adults with spina bifida, particularly the severe form or myelomeningocele, may have sleep apnea or other sleep disorders.
Tethered spinal cord: Tethered spinal cord occurs when the spinal nerves join the scar where the defect was surgically closed. When this happens, the spinal cord does not grow properly as the child grows. This progressive anchoring can lead to loss of muscle function in the legs, bowel, or urinary bladder. Surgery can limit the degree of disability.
Chiari type II malformation: This is a common brain abnormality in children with myelomeningocele. It occurs when the brain stem, or the lowest part of the brain above the spinal cord, is lengthened and positioned lower than it should. This can cause problems with breathing and swallowing. In rare cases, compression occurs in this area of ?? the brain and surgery is needed to relieve the pressure.
Skin problems: Children with spina bifida can suffer injuries to the feet, legs, buttocks, or back. They cannot feel when a blister or sore appears. Sores or blisters can turn into deep wounds or foot infections that are difficult to treat or heal. Children with myelomeningocele are at increased risk for cast wound problems.
Shunt malfunction: Shunts placed in the brain to drain fluid build-up in the brain can become infected. Warning signs may vary from child to child, but some of them may include: headaches, vomiting, irritability, swelling or redness along the shunt, mental confusion, eye changes (staring down), difficulty feeding, or seizures.
If you see any of these signs in your baby or child, seek medical attention immediately.
Treatment for spina bifida.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for spina bifida. The nerve tissue is already damaged and is hard to be repaired, nor can a function be restored to the damaged nerves. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the disorder. Generally speaking, children with the mildest form of spina bifida need no treatment, although some may require surgery as they grow.
In the womb, the surgery is considered experimental, and there are risks to the fetus as well as to the mother. The significant risks to the fetus are those that might occur if the surgery stimulates premature birth. Those risks are organ immaturity, brain hemorrhage, or death. Risks to the mother include infection, blood loss leading to the need for transfusion or gestational diabetes.
The good news is that the benefits of surgery are promising and include less exposure of the vulnerable spinal nerve tissue and bone to the intrauterine environment, in particular the amniotic fluid, which is considered toxic.
Some children will need subsequent surgeries to manage problems with the feet, hips, or spine. Individuals with hydrocephalus generally will require additional surgeries to replace the shunt, which can be outgrown or become clogged or infected.
Related posts.
How to deal with gestational diabetes for a healthier pregnancy.
What to expect from your fetal anatomy scan and how to prepare.
The first trimester must do’s to achieve a healthy pregnancy.
Final thoughts about Spina bifida ultrasound.
In children with spina bifida, the prognosis, activity, and participation depend on the number and severity of abnormalities and associated personal and environmental factors. But most children with the disorder have average intelligence and can walk, often with assistive devices. If learning problems develop, appropriate educational interventions are usually helpful.
I hope this article was helpful to you, as usual, thanks for reading it.
Zadi, xo
Disclaimer: The medical information on this post is for educational and entertainment use only. Under no circumstances, this information is to replace your doctor’s advice or to treat any disease. For proper care, always visit your doctor.










Hi there, if you use WordPress there are a few plugins you can use to avoid the copy of your content right from the web. I suggest you to check that out. Is easy to download and it’s been effective for me so far. Best of lucks to you.
Indeed. Thanks Soffi
Valuable information. Lucky me I found your web site by accident, and I’m shocked why this accident didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Hello my friend! I want to say that this post is amazing, great written and come with approximately all significant infos. I would like to look extra posts like this .