Of all types of ovarian tumors, Teratoma is unique and rare. Even so, it develops in many women. In this post we are going to talk about everything you need to know about teratomas, and how ultrasound is one of the most useful tools to make the diagnosis. Ultrasound images with explanations are included in this post.
What is a teratoma?
Teratoma is a rare type of tumor, which can contain fully developed tissues and organs such as hair, teeth, muscle or even bones inside. Although teratomas develop in any part of the body, they are more frequent in the tailbone or coccyx (the final segment of the spine), ovaries and testicles for males.
Teratomas can develop in everyone, including newborns, children, and adults. But they are more frequent in women.
What are the symptoms of a teratoma?
Teratomas can go unnoticed for years. Usually does not even show any symptoms. Once the symptoms begin to develop, they will depend on the location of the teratoma.
The most common signs and symptoms of teratoma are usually:
- Pain.
- Swelling.
- Bleeding.
- High levels of the hormone known as Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP). This hormone only rises during pregnancy, so an elevation in the absence of it is not normal.
- High levels of the hormone Beta-human Chorionic gonadotropin or BhCG. Another hormone that in the absence of a pregnancy should not be increased.
What are the different types of teratomas?
Teratomas are classified as mature or immature.
Mature teratomas: They are generally benign, which means they are not cancerous. But after surgery, they have the risk of growing again.
Immature teratoma: They are more likely to develop a malignancy.
Therefore, in the presence of a teratoma, it is always important and recommended to visit the doctor immediately.
In the case of mature teratomas, an additional classification is used
Cystic: Wrapped by a sac of its own, which contains fluid.
Solids: Composed of different types of tissues, as mentioned before (Hair, teeth, muscle or even bones). This type of teratoma is not wrapped in a sac.
Mixed: Composed of liquid and tissue.
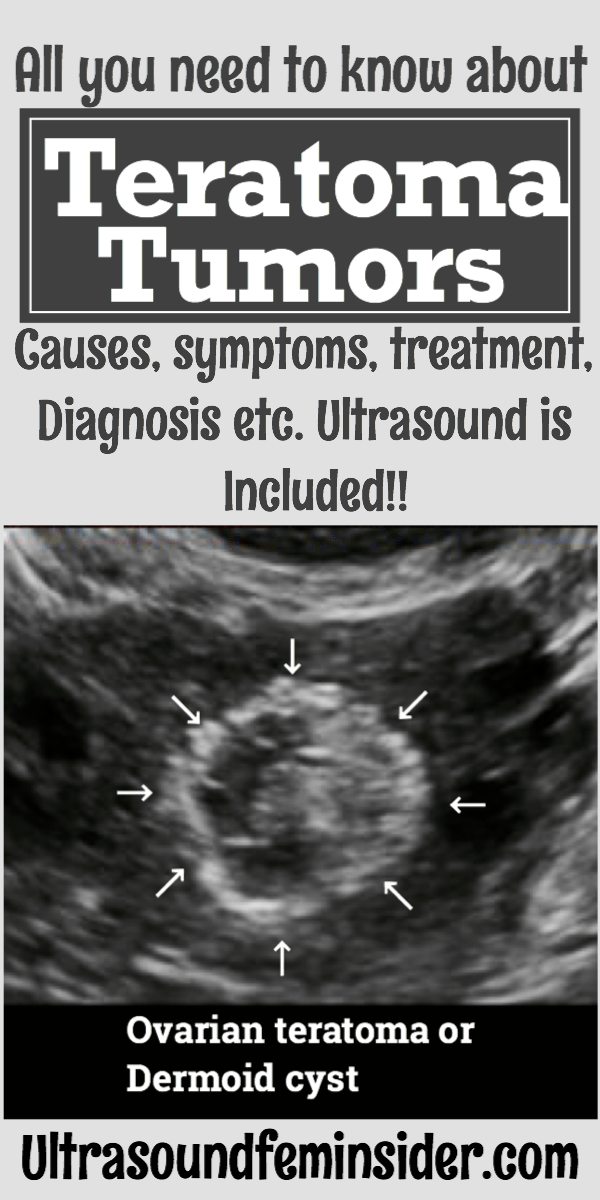
Mature cystic teratomas are also known as Dermoid cysts.
Teratoma symptoms depend specifically on the location.
The sacrococcygeal teratoma or tailbone is the most frequent among newborns and young children.
Although it is still considered rare, it is still found in 1 in 40,000 children according to a recent study.
This type of teratoma can develop inside or outside the body in the coccyx area. And the symptoms may include
- Palpable and visible mass in this area.
- Constipation.
- Pelvic and/or abdominal pain.
- Painful urination.
- Swelling of the public area.
- An abnormal weakening of the legs.
Specific symptoms of teratomas developed in the ovary may include.
- Pelvic and abdominal pain that can become intense.
- Pressure in the ovaries, which may be related to ovarian torsion, a condition that develops when the blood supply of the ovary is decreased or absent by a torsion of the ovary, caused by the weight of the mass inside the ovary.
- In rare cases, the teratoma of the ovary may be accompanied by encephalitis, which can lead to severe headaches, psychiatric symptoms, and psychosis.
Specific symptoms of teratomas developed in the testicle may include.
Testicular teratoma is more common among patients of 20 to 30 years of age. And the most frequent symptom is
- Palpable mass of the testicle.
- Swelling of the testicle.
Pin it for later.
Related posts:
Irregular periods. Causes, treatment, natural remedies, ultrasound and more.
Pelvic pain in women. Role of ultrasound diagnosing pelvic pain.
All about Polycystic ovarian syndrome or PCOS.
Ovaries, hormonal cycles and common cysts.
Uterine Fibroids, how to naturally treat and prevent them.
Causes of teratomas.
Teratomas develop from a complication in the process of development and growth of the different tissues of the body during the germinative stage, which means that, a teratoma forms even before a baby is born. Teratomas develop from the body’s germ cells.
Other theories suggest that teratomas are a condition that originates within the primordial germ cells. This is known as the pathogenetic theory. This explains in some way why teratomas can have tissues such as wax, hair, teeth. The location of the teratomas also varies depending on the germ cells that gave rise to it.
What you need to know about teratomas and cancer?
As mentioned earlier, teratomas are classified as mature (usually benign) and immature (usually cancerous). The possibility that the teratoma is malignant or not, depends on the characteristics of the tumor and the location in which it is developed.
Sacrococcygeal teratoma or SCT.
This type of teratoma is 20% of the time immature (usually cancerous). And even in cases where they are benign, surgery will always be the ideal treatment, as the location and characteristics of the tumor can cause many symptoms or complications. This type of teratoma is very rare, and in most cases, it is found in newborns.
Ovarian teratoma.
The vast majority of ovarian teratomas are mature (benign). Mature ovarian teratomas are also known as Dermoid cyst (You will see ultrasound images related to a dermoid cyst in this article below).
Only 1 to 3% of ovarian teratomas are cancerous, which is excellent news. This type of teratoma goes unnoticed throughout life until women reach the reproductive stage.
Immature ovarian teratomas (cancerous) are very rare and are usually diagnosed in girls at an early stage of puberty, usually before 20 years of age.
Teratomas of the testicle.
This type of teratoma carries an additional classification and is pre-puberty or post-puberty.
Pre-puberty or pediatric teratomas are usually mature (benign).
Post-puberty or those that develop in the adulthood of men are generally immature or malignant. Therefore, they require urgent attention since about 2/3 of the men who are diagnosed with testicular teratoma have advanced stages of cancer metastasis.
Teratomas diagnosis.
Due to the great variety of signs and symptoms of teratomas, it is easily diagnosed.
To diagnose a teratoma, doctors must collect information on different tests including X-ray, Ultrasound or CT scans of the pelvis, accompanied by blood tests to detect elevations in hormones such as AFP and BhCG.
In newborn babies, one of the first things checked by the pediatrician in the first medical consultations is sacrococcygeal teratoma. After this initial examination at the pediatrician, if all is well, then there are no risks.
Teratomas of the ovary are usually diagnosed in women in the reproductive stage. Although this type of teratoma is not malignant and usually does not show symptoms, in most cases is accompanied by pelvic pain, due to the size of the teratoma.
The testicle teratoma is usually detected in physical exams with the doctor, where the doctor can detect palpable mass in the testicle, and therefore sends the corresponding exams.
Here are some ultrasound images where you will be able to see all types of Teratomas.
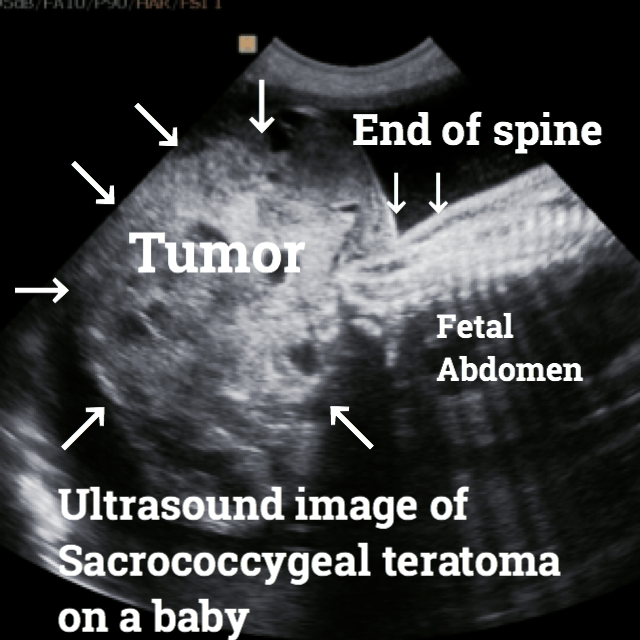
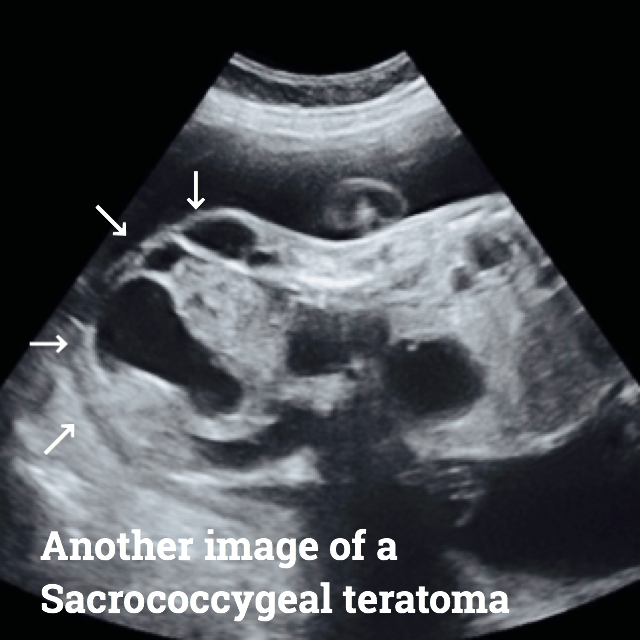
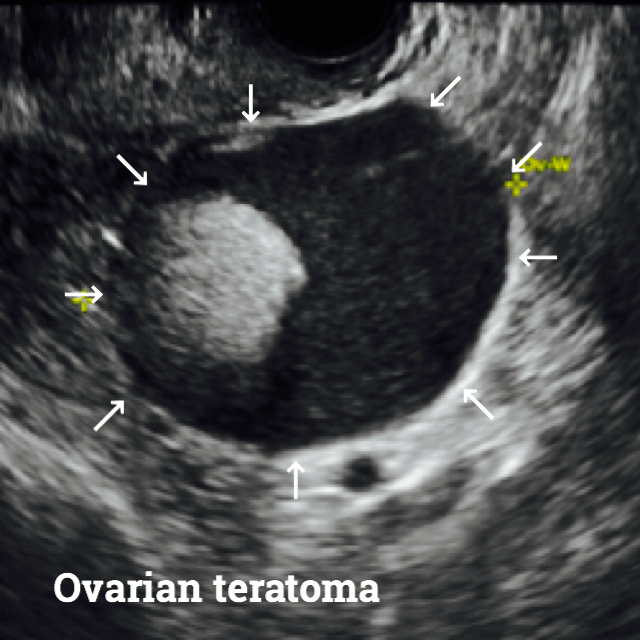
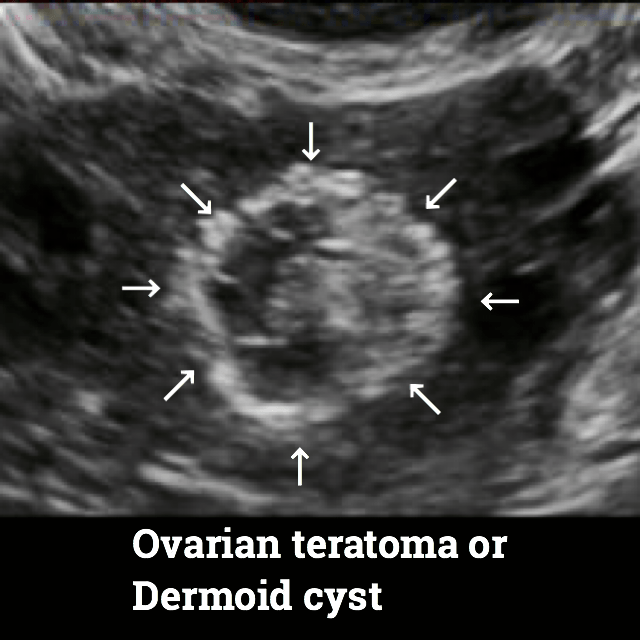
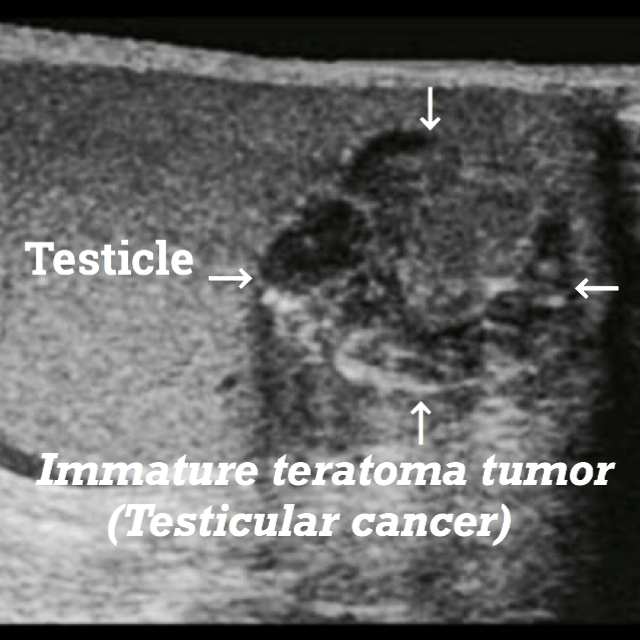
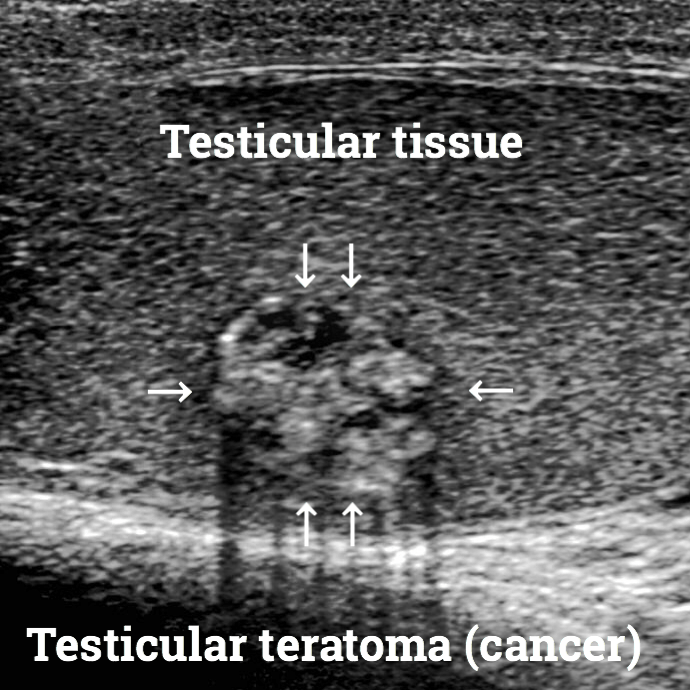
Teratomas treatment.
In the case of sacrococcygeal teratoma, is usually detected during pregnancy, it is followed closely with frequent ultrasounds.
If the size of the teratoma is small, and no other complications are observed in the baby, and it does not grow too large, in this case, a vaginal delivery can be performed. On the other hand, if the teratoma is large in size or other complications follow the diagnosis, then an early cesarean section will be planned.
The sacrococcygeal teratoma is corrected through surgery once the baby is born. And it is also monitored for the high probability of recurrence for up to 3 years after surgery. If the teratoma is confirmed as malignant, chemotherapy will be performed on the baby. Survival rates today are excellent for this type of tumor.
Teratoma of the ovary or dermoid cyst is also treated by laparoscopic surgery. This involves a very small incision in the abdomen to introduce the instruments.
The risks associated with this surgery are really low. The most important risk is to prevent the tumor from breaking down because this can cause spillage of the content in the pelvic area which can produce a condition known as chemical peritonitis.
In some cases, it may be necessary to remove part of the ovary. In only 25% of cases, teratomas are found in the 2 ovaries, which can have a negative impact on a woman’s fertility later on.
For immature (malignant) teratomas, most cases are cured today with a combination of surgery and chemotherapy.
In the case of teratoma testicular, the first treatment option is surgery, followed by chemotherapy. Male fertility in testicular teratomas is always affected.
In conclusion Teratoma Tumors.
Teratomas are rare and benign in most cases. In the last decade the treatments for cancerous teratomas have been perfected to the point that today, in most cases the teratomas can be cured.
Keeping you informed and visiting a competent health professional is the best option to get the best treatment and outcome.
Thanks for reading this article. If you need to ask a question, leave me your comment below.
Zadi, xo
Disclaimer: This post is not intended to diagnose, treat, prevent, or cure any disease. For proper medical attention, please visit your physician.










kyukyuwai96@gmail.com
[…] Teratoma. Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. […]
My 10 year old daughter has been diagnosed with teratoma in the ovaries. Guess she is the one in 40000 and she is 10 years old. Whats the best option you would recommend surgery or chemotherapy and which one first?
Hi Linda, The answer to your question depends on how big is the mass on the ovary. Here is my answer for you, if the mass is relatively small and is well encapsulated, I would recommend surgery and perhaps if is needed chemo. Always talk to the doctor about your options. Thanks and good luck.
Informative and interesting. Thank you so much.
Do you have a spam issue on this site; I also am a blogger, and I
was curious about your situation; many of us have developed some
nice procedures and we are looking to exchange methods with other folks,
be sure to shoot me an email if interested.
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The total glance of your site is excellent, let alone the content!
You made some decent points there. I appeared on the web for the problem and found most people will go together with along with your website.
Valuable info. Fortunate me I found your web site accidentally, and I am shocked why this twist of fate didn’t took place earlier! I bookmarked it.
After examine a couple of of the blog posts in your website now, and I actually like your approach of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark web site record and will likely be checking again soon. Pls try my web site as effectively and let me know what you think.
Are you a Fibroid victim? Reach out to Dr. Uduehi for pamanet cure once and for all at: uduehiherbalcare@gmail.com (+234 706 607 4917)
Thank you so much. I do the articles myself.