The term “retained products of conception” (RPOC) refers to placental and/or fetal tissue that remains in the uterus after a miscarriage, an abortion, or a premature or full-term delivery. Retained products of conception (RPOC) are something that can happen after a pregnancy is terminated early or in the middle of the first trimester, as well as after a vaginal or cesarean delivery. It is often accompanied by persistent bleeding, pain in the pelvic region, and infection if not treated appropriately. In this article I am going to give you important information about Retained Products of Conception (RPOC), and we are also talking about how Retained Products of Conception (RPOC) can affect fertility. In this article I am showing also Ultrasound images of Retained Products of Conception (RPOC), so you know what to look for. Ready? Let’s get started.
Retained Products of Conception (RPOC). What is it and How Affects Fertility.
According to studies, RPOC was present after a third-trimester delivery in about 3% of women only, whereas it was diagnosed after pregnancy termination or miscarriages during the second and first trimesters in 40% and 17% respectively. Meaning that RPOC is more common during the first and second trimester than after a full-term delivery on the third trimester.
What Factors Contribute to the Retention of Products of Conception?
The placenta is an organ that forms inside of a woman’s uterus when a fetus grows inside of it. Your uterine wall is where it is linked to this structure. Through the placenta and the umbilical cord, it supplies your unborn child with oxygen and nutrition. The placenta and any other tissues that form inside the uterus during pregnancy will normally be expelled from the body during the process of giving birth. Nevertheless, there is a possibility that part of the tissue will remain in the uterus. The uterus will not be able to go back to the pre-pregnancy state if there is RPOC present.
What Symptoms may you Expect to have if you Develop Retained Products of Conception?
Following a pregnancy, your body will go through a significant number of physiological transitions. It is common to experience some bleeding and vaginal discharge. But prolonged or heavy bleeding after pregnancy or blood clots are potential warning signs of RPOC.
Postpartum hemorrhage, often known as vaginal bleeding after childbirth, is the symptom of RPOC that occurs the most frequently. Other possible symptoms include the following:
- Enlarged in size uterus.
- Fever.
- Infection.
- Open cervix (the opening between vagina and uterus should be small or closed after pregnancy).
- Pelvic Pain.
You can share this article by clicking the image below.
How can Doctors Identify Cases of Retained Products of Conception?
It is not often easy to diagnose RPOC based just on the patient’s symptoms. There is a possibility that the symptoms are comparable to those of other postpartum health conditions. The diagnosis of RPOC can be made more certain with the help of the following examinations and testing.
Tests on the blood and the tissues:
- Test for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG): This test determines the concentration of the hCG hormone that is present in your blood. This hormone is produced by the placenta. RPOC may be the reason of elevated levels of the hormone hCG.
- Endometrial biopsy: An endometrial biopsy involves your healthcare provider removing a tiny sample of tissue from your uterus in order to analyze its structure and function. Under a microscope, they examine the tissue in question. The existence of chorionic villi, which are cells that are found in placental tissue, indicates that placental tissue is still present in the uterus.
Imaging exams Done to Confirm RPOC.
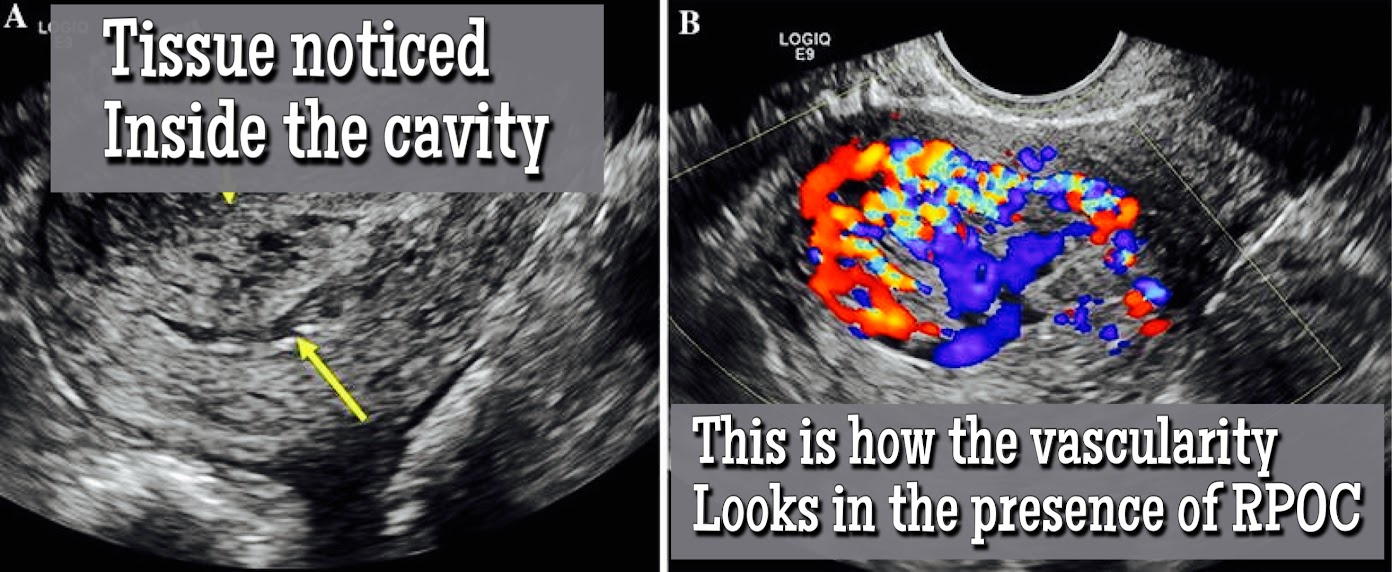
- A transvaginal ultrasound: A type of imaging exam that involves inserting an ultrasonic probe into the vagina in order to examine the uterine lining. Through a transvaginal ultrasound a color Doppler can be utilized. This will demonstrate whether or not the additional tissue in the uterus still possesses a blood supply. The presence of a blood supply may be an indication that placental tissue is still attached to the uterine cavity.
- Hysteroscopy: A hysteroscopy involves your healthcare professional inserting a thin, lighted tube into your vagina in order to examine the uterus. They look for abnormal tissue inside the cavity or other issues.
There are 3 categories of RPOC.
- Type 1: Minimal endometrial vascularity less than the myometrium.
- Type 2: Moderate vascularity with nearly equal endometrial and myometrial vascularity.
- Type 3: Marked endometrial vascularity more than adjacent myometrium.
What Treatment is Utilized to Treat RPOC?
There are many therapies available for RPOC, including the following:
- Misoprostol: Is a medication given to the patient to allow the body to naturally expel the abnormal tissue inside the linning. This medication can be given either orally or through the vaginal canal.
- D&C stands for dilation and curettage, which is a term used to describe a very simple surgical procedure that removes the contents of the linning of the uterus in the case the treatment was not successful. Your healthcare professional will first dilate (open) your cervix, and then they will remove tissue with either a curette (a small surgical tool) or suction.
Side Effects of the Treatments?
There are no major side effects associated with the use of misoprostol (significant bleeding can occur as complication from misoprostol, but this is very rare). However, D&C presents a higher risk of:
- Heavy Bleeding.
- Developing an Infection.
- Uterine Perforation (The condition known as perforation is uncommon. Most of the time, the uterine wall will heal on its own).
- Formation of Adhesions can happen, this is known as uterine scarring. Scarring on the uterine lining might affects the woman’s fertility.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
If you have any of the following symptoms after having a baby, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible:
- Having a hard time breathing.
- Heavy vaginal bleeding that after a few weeks is not getting better or is getting worse.
- You start experiencing High temperature.
- Symptoms of nausea and vomiting.
- Severe pelvic pain.
Related Posts you might want to read!
First trimester of pregnancy. The checklist.
How to Conceive a Girl Naturally.
25 Most Common Pregnancy Questions Answered.
Final Thoughts about Retained Products of Conception RPOC.
There is no way to stop or prevent RPOC from occurring. You can, however, take steps to ensure that your healthcare practitioner is aware of your whole medical history. You may have an increased likelihood of developing RPOC as a result of previous difficulties during pregnancy or surgical procedures inside the uterus, or history of disease such as PID. If this is the case, the members of your care team will keep a close eye on your overall health both during and after any further pregnancies you have. The good news is that, after receiving therapy for RPOC, the vast majority of women are still able to have children and have good pregnancies.
I hope this article is helpful, share your thoughts bellow.
Zadi, xo
Disclaimer: The medical information on this post is for educational and entertainment use only. Under no circumstances, this information is to replace your doctor’s advice or to treat any disease. For proper care, always visit your doctor.










This website is actually a walk-through its the knowledge it suited you in regards to this and didn’t know who to question. Glimpse here, and you’ll absolutely discover it.