From all the things that must be almost perfect during pregnancy, one of them must be the amniotic fluid. But, have you ever wondered why the amniotic fluid is so essential for the life and development of your baby in the womb? If you are here, probably yes. If that’s the case, stay with me, because in this post, I am going to tell you everything you should know about amniotic fluid, and how to interpret an ultrasound in case you need to have one done. Ready? Let’s begin!
What is the amniotic fluid?
A pregnancy is made up of 2 membranes: the amnion and the chorion. The outermost of the two fetal membranes is the chorion, the chorion invade and destroy in a way the uterine decidua to absorb from it nutritional materials for the growth of the embryo while the amnion is the innermost membrane or fetal basalis, therefore the membrane that surrounds the embryo.
The amniotic liquid begins to form from the beginning of pregnancy (week 12, more or less). However, the consistency changes during the pregnancy from a watery liquid to a more urine type of liquid, and that is because when the digestive system develops within the fetus, they start swallowing and urinating amniotic fluid thought out the pregnancy.
What are the functions of the amniotic fluid?
Amniotic fluid has multiple functions that are essential for the proper development and growth of a baby. Among these crucial functions you’ll find:
- Protection of the fetus: The amniotic fluid acts as a cushion that protects the fetus from impacts and external pressure; it basically serves as a shock absorber.
- Lubrication: It acts as a lubricant that prevents parts of the fetal body from merge or form together, therefore preventing fetal malformation.
- Umbilical cord support: Prevents the umbilical cord from being compressed by the baby. Remember that the umbilical cord is the one that carries nutrients and oxygen to the baby from the mother, and brings the baby waste to the mother to be excreted.
- Temperature control: The amniotic liquid acts as an insulator that, regardless of the temperature outside, it maintains a constant, optimal, and warm temperature inside the womb for your baby.
- Infection control: The amniotic fluid provides antibodies that keep the baby free of external infections.
- Facilitates muscles and bone development: Once the baby is formed, the different parts of the body need mobility to develop appropriately, the amniotic fluid allows this space where the baby can move.
- Lung and digestive system development: During pregnancy, the baby practices respiratory and swallowing movements, thus allowing the muscles of these two systems to develop correctly as well.
What are the normal and abnormal values of amniotic fluid?
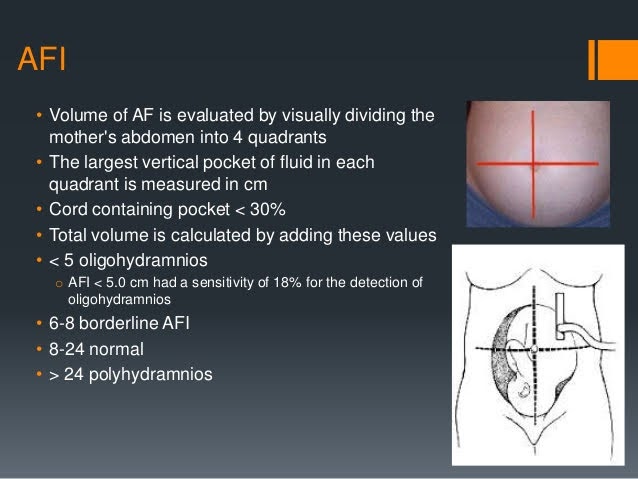
Usually, amniotic fluid levels fluctuate during pregnancy. Normal amniotic fluid levels range from 5 centimeters to 24 centimeters.
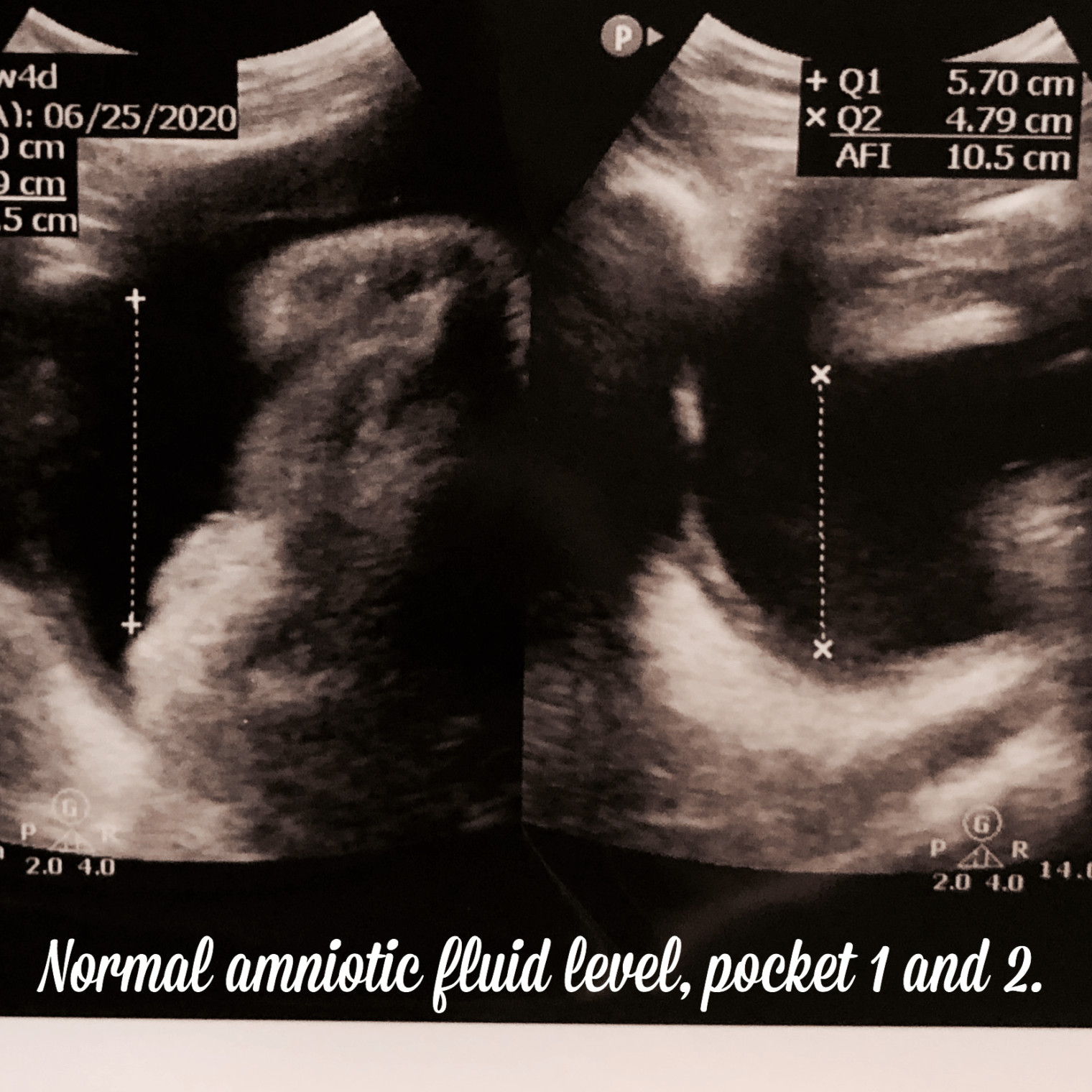
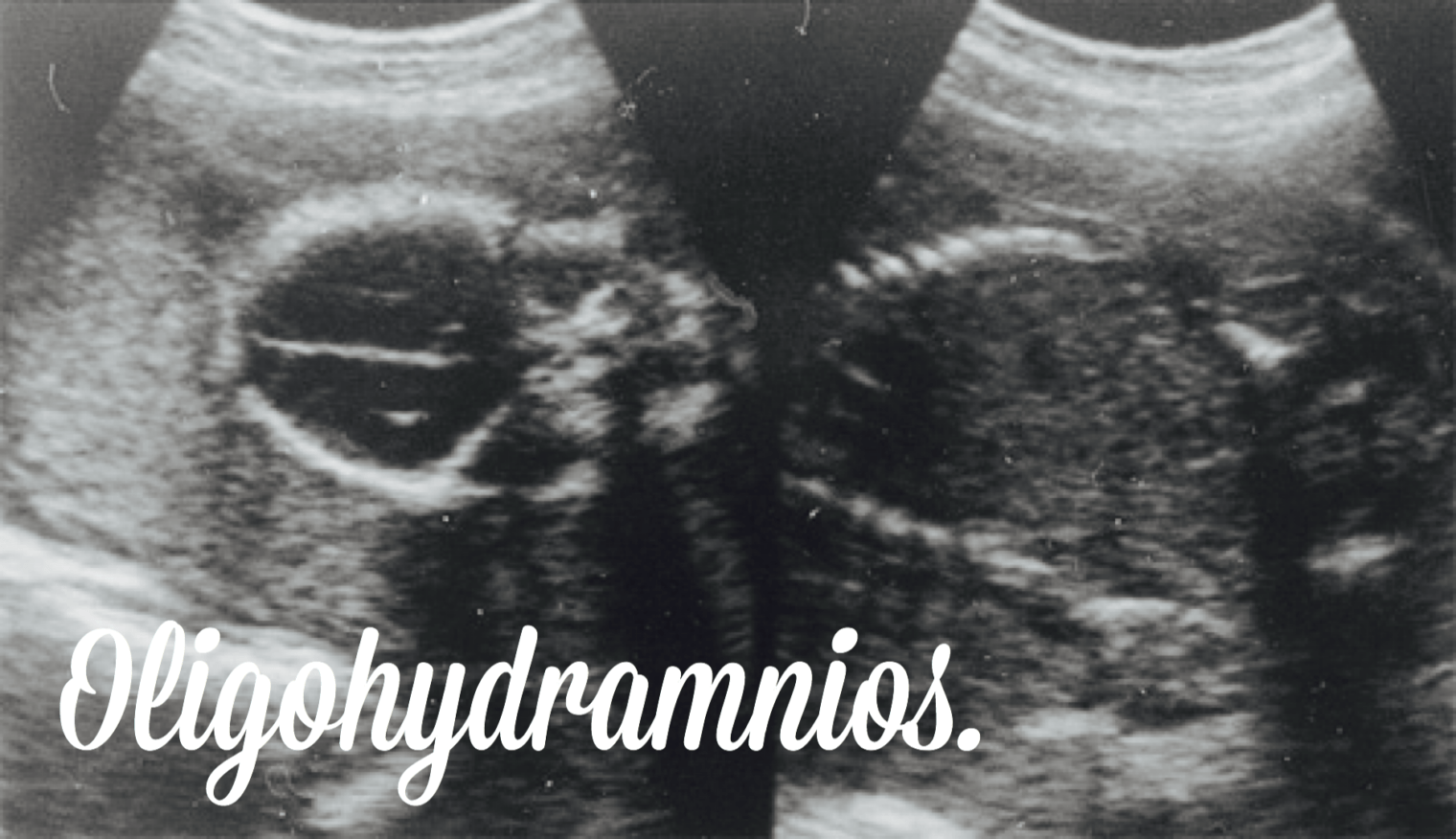
- When amniotic fluid values are below 5 cm, or the maximum vertical pocket measurement is less than 2 cm, this is known as Oligohydramnios. (low fluid)
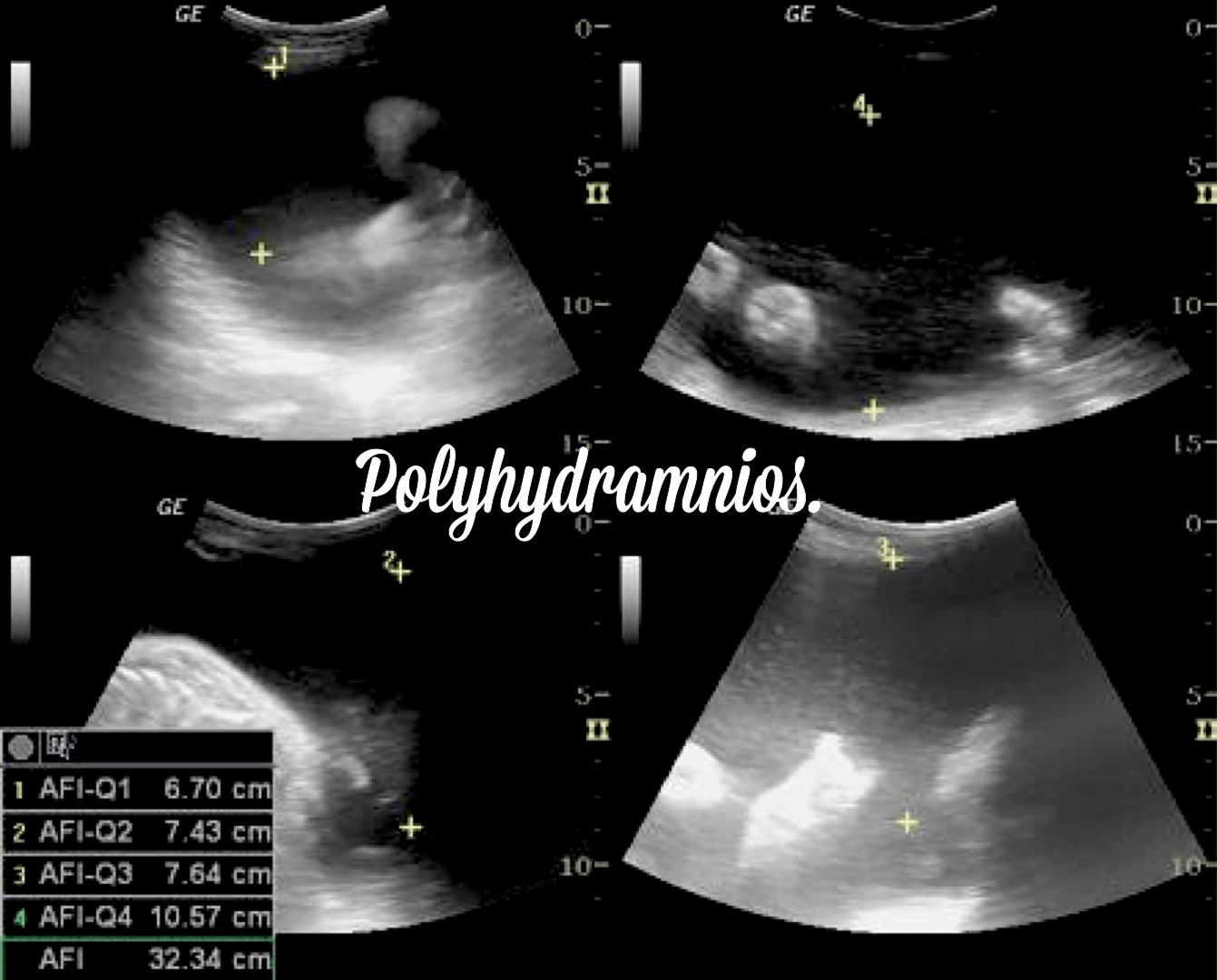
- When amniotic fluid values are above 24 cm, this is known as Polyhydramnios. (excess of fluid)
Risk factors for developing Oligohydramnios?
Pregnant women who are more likely to develop Oligohydramnios include those with one or more of the following medical conditions.
- Hypertension.
- Preeclampsia.
- Gestational diabetes.
- History of previous pregnancy with Fetal growth restriction.
- Placental abruption.
- Lupus.
- Multiple fetuses, such as twins or triplets.
- Fetal kidney genetic abnormalities.
- Past due and still pregnant. More than 40 weeks pregnant.
An abrupt decrease in amniotic fluid can also occur due to a premature rupture of the membranes, which causes a leaking and, therefore, a reduction in the amount of fluid within the gestational sac.
How you know if you have amniotic fluid leaking?
- You might feel like a gush of warm fluid coming from the vagina.
- Or it might feels like a slow trickle of warm fluid.
It will usually be clear and odorless but may sometimes may contain traces of blood or mucus. If the liquid is amniotic fluid, it is unlikely to stop leaking.
Share the post.

When not to be concerned.
The uterus sits on top of the bladder during pregnancy. Therefore, one of the common symptoms for pregnant women is leaking urine. If the discharge smells like urine, is probably not amniotic fluid.
When to be concern and call the doctor.
If the fluid does not appear to be urine or vaginal discharge, it is best to check with your doctor.
Women who also experience the following symptoms should seek medical attention immediately:
- Foul-smelling, brown or green discharge from the coming from the vagina.
- Low grade or high fever.
- Your uterus is feeling tender.
- You are experiencing rapid heart rate.
- The baby hasn’t move in a 24 hour full period.
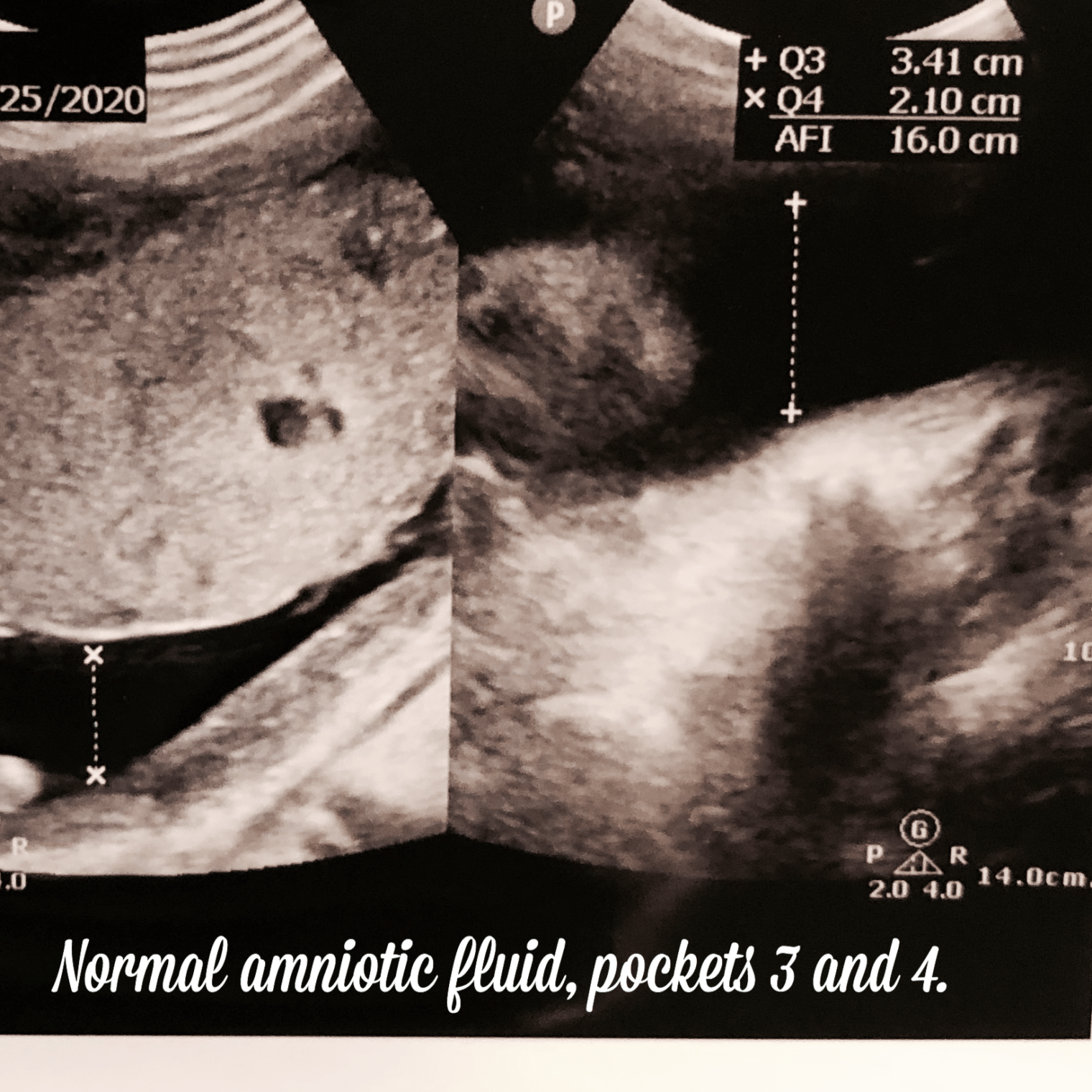
Let’s talk about Polyhydramnios.
As I mentioned before, Polyhydramnios is the condition where the amniotic fluid levels are increased or above 24 cm. This condition might be the result of Fetal disorder or malformations, such as:
- Gastrointestinal disorders such as Gastroschisis, Diaphragmatic hernia, atresia duodenal or esophageal.
- Achondroplasia, a bone growth disorder.
- Brain disorders, such as Anencephaly.
- Fetal heart problems.
- Fetal lung abnormalities.
- Hydrops fetalis (a condition where there is an abnormal accumulation of fluid inside the baby’s body).
- Congenital growth disorders.
- Fetal infections.
- Blood incompatibility between mother and child. (RH incompatibility)
- Twin-to-twin transfusion (is found in a twin pregnancy when a child gets more blood flow compared to the other).
- Multiple pregnancy (twin or triplets).
Within the maternal complications due to Polyhydramnios, you’ll find:
- Preterm labor.
- Premature rupture of membranes.
- Stillbirth.
- Cord prolapse.
- Placental abruption.
- Postpartum hemorrhage.
Regardless of the complications associated with polyhydramnios, this condition is also associated with fetal macrosomia (big babies). In macrosomic cases, in the absence of fetal malformations or maternal complications, and if the patient is asymptomatic, it is not worrisome, only closed monitoring will be necessary.
How is the amniotic fluid measured during the ultrasound?
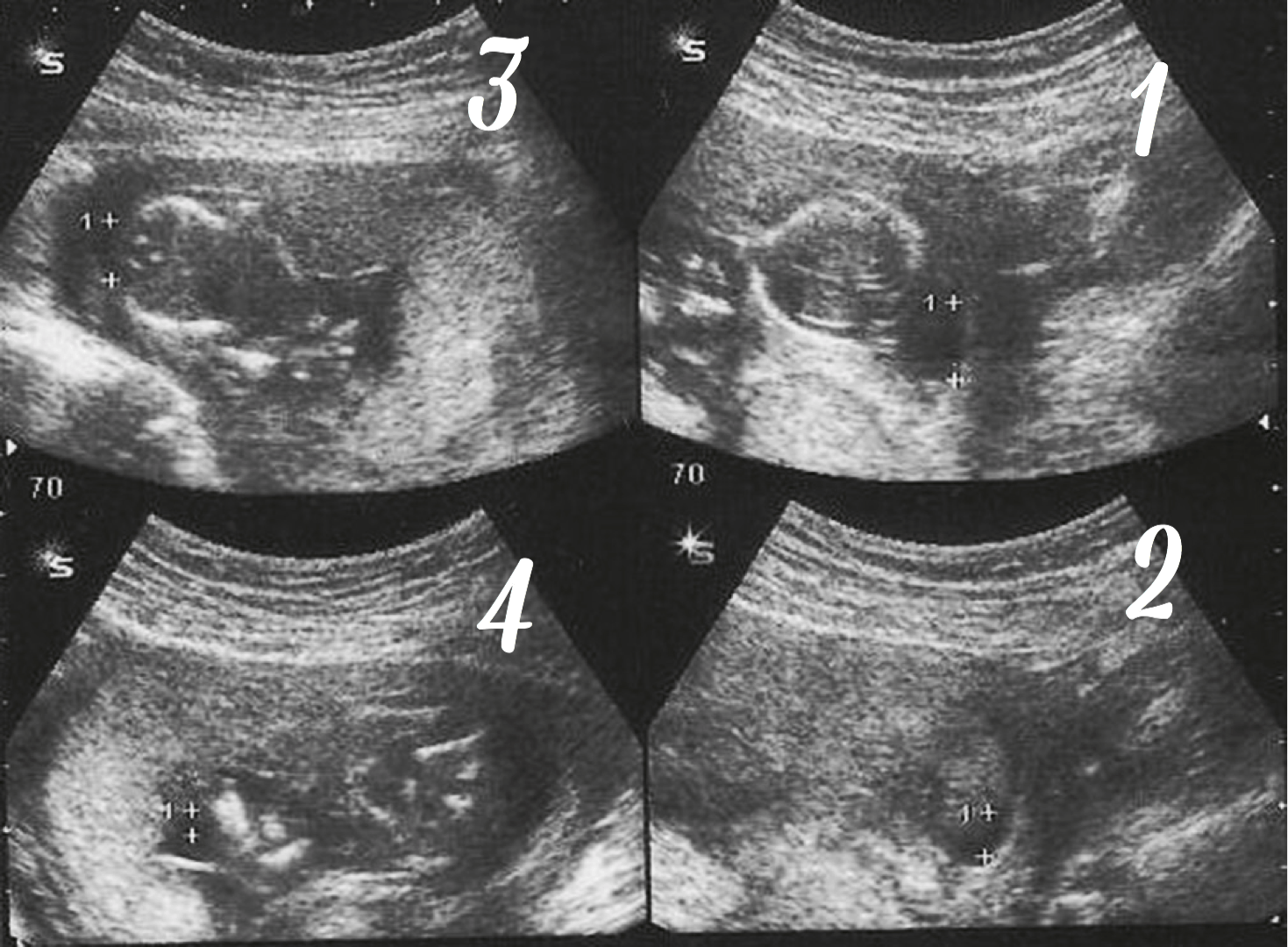
To monitor amniotic fluid levels, the fastest and most accurate technique available is ultrasound. The amniotic fluid is measured in 4 different quadrants or pockets during the ultrasound, the measurement is taken vertically, and it must be clean, without organs or umbilical cord in the liquid pocket.
Tips to prevent amniotic fluid abnormalities.
- Start your pregnancy with proper care to your body. (vitamins)
- Treat and control your pre-existing conditions before staring a pregnancy, if possible.
- Avoid taking medications or recreational drugs that could potentially put your pregnancy in danger.
- Stick to a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy.
- Get a medical appointment as soon as you know you are pregnant.
- Don’t skip or miss your prenatal check-ups.
- Stay hydrated at all times, drinking a lot of water will prevent Oligohydramnios (low amniotic fluid).
- If you have any medical conditions like hypertension, lupus, diabetes, etc. follow the recommendations from your doctor closely.
- Always contact your doctor if the baby is not moving as usual, or if you are noticing any leaking of fluid.
- Plenty of rest may help to improve the blood flow to the placenta, which will help your body to regulate itself the levels of amniotic fluid in non-severe cases.
You might be interested in these other posts:
Ways to relieve morning sickness during pregnancy.
How to create the perfect nursery for your baby on a budget.
How to prevent preterm labor naturally.
Third trimester weeks, the ultimate checklist.
Normal 35 week pregnancy and ultrasound, your complete guide.
Treatment for amniotic fluid abnormalities.
For the two amniotic fluid abnormalities, a recommended first step is frequent fluid monitoring with ultrasounds and visits to the doctor.
Any of the two amniotic fluid abnormalities, if they occur in the second trimester, the risks are greater for birth defects, loss of pregnancy, preterm labor, or neonatal death. On the other hand, if they occur in the third trimester, or near delivery, complications are almost non-existent with an excellent prognosis.
Regarding the treatment that can be foreseen to Oligohydramnios (low fluid), they are:
- Drink up lots of fluids: The more you drink, the better. This is not only will help your placenta with the production of amniotic fluid but also will assist your organs to work efficiently.
- IV fluid: In severe dehydration cases due to nausea and vomiting, the doctor may recommend an IV for increased your amniotic fluid more quickly.
- Amnio-infusion: This treatment can only be given to women when they are already in labor, and where the membranes are already broken, it consists of instilling a special liquid inside the gestational sac to facilitate a delivery without complications.
- Early delivery: Mainly for women in the second or early third trimester, if the lack of amniotic fluid can threaten the life of the fetus, a premature delivery will be necessary.
Among the treatments for severe cases of Polyhydramnios, you’ll have:
Drainage of excess amniotic fluid: Your gynecologist may use amniocentesis to drain the excess of amniotic fluid from your uterus. This procedure, like any other procedures, may involve risks, including preterm labor, placental abruption, and premature rupture of the membranes.
Use of a medication: Your doctor may prescribe the oral medication to help reduce fetal urine production and, therefore, the amniotic fluid volume. This medication isn’t recommended beyond 31 weeks of pregnancy. Due to the risk of fetal heart problems, your baby’s heart may need to be monitored with a fetal echocardiogram and Doppler ultrasounds regularly. Other side effects of this medication may include nausea, vomiting, acid reflux, and inflammation of the lining of the stomach (gastritis).
An early delivery is always another resource in case a premature membrane rupture occurs, and the life of the baby is in danger.
Final thoughts.
The take away from this article is that amniotic fluid abnormalities can occur in any trimester of pregnancy. Although there is no specific cure, there are little things you can do before and after you are pregnant to avoid having any complications.
It is always good to contact your doctor in case you have any questions.
I hope you have learned something about this article. Leave me in the comments if you have had before or are going through this experience at the moment.
Zadi, xo
Disclaimer: The medical information on this post is for educational and entertainment use only. Under no circumstances, this information is to replace your doctor’s advice or to treat any disease. For proper care, always visit your doctor.









so nice share this post under this mention to clear way
Thank you so much Laxman
Great post, love the ultrasound images. Thanks
My spouse and I stumbled over here different page and thought I should check things out. I like what I see so now i’m following you. Look forward to looking into your web page again.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You clearly know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your site when you could be giving us something informative to read?
This is very interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your fantastic post. Also, I have shared your site in my social networks!
[…] The Volumen of the amniotic fluid, this is measured in 4 pockets in the belly. Each pocket is measured vertically, for this part to be considered normal at least one of the four vertical pockets of amniotic fluid has to measure 2 cm or more. A Volumen of amniotic fluid below 5 cm in total means that the amniotic fluid is low, this condition is known as Oligohydramnios, Read this other article to learn more about Amniotic fluid. […]
[…] a biophysical profile will be extremely helpful to evaluate fetal breathing, movement, tone and Amniotic fluid, all those signs speak about your baby’s wellbeing. Also, a Doppler Ultrasound will be helpful […]
[…] All you need to know about amniotic fluid. […]