You’ve probably heard of the placenta at some point in your life, mostly if you’re pregnant. And that is because the placenta is a fundamental organ for the development of a normal pregnancy. The placenta forms in the first trimester and is able to start performing its role as early as 13 weeks of gestation. In this article we are going to be talking more deeply about placenta previa. What is it, causes, how it is diagnosed and how it looks on an ultrasound and most importantly How does Placenta Previa Affect a Pregnancy. So if you are looking for in deep reliable information about placenta previa keep reading because this article is going to answer a lot of questions you may have. Ready? Let’s begin.
Let’s do a quick recap about what is the Placenta.
During pregnancy, the placenta acts as a transitional organ that connects the developing baby to the mother’s uterus. Soon after conception, the placenta begins to form and will eventually become attached to the inner lining of the uterus. The umbilical cord is what links your unborn child to the placenta while they are still in the womb. Your unborn baby depends on the placenta and umbilical cord to stay alive while they are still within the uterus.
How does Placenta Forms?
About seven to ten days after conception, when an egg that has been fertilized implants in the uterus, the placenta starts to grow. It keeps getting bigger to support your baby while you’re pregnant.
The implantation of the fertilized egg into the lining of the uterus marks the beginning of the development of the placenta. The majority of the placenta is composed of blood arteries, which are housed within structures known as villi. Through the umbilical cord, the blood vessels are connected to the bloodstream of the developing baby. The remainder of the placental tissues are mostly responsible for connecting the villi to the umbilical cord.
Placental Functions.
- Provides oxygen and nutrients to your baby.
- It gets rid of your baby’s harmful waste and carbon dioxide.
- Helps your baby grow by producing hormones.
- Gives your baby the same immunity you have.
- Helps keep your baby protected from infections and pathogens.
- Contributes to the formation of amniotic fluid.
Different Normal Locations in which Placenta will Form.
- Posterior: It grows on the back wall of the uterus.
- Anterior: It grows on the front wall of your uterus, which is closest to your abdomen.
- Fundal: It grows at the top of your uterus, in the fundus.
- Lateral: It grows on the right or left side of the uterine wall.
Share this article.

Abnormal Locations in which Placenta could form.
- Accreta: When the placental villi attach to the myometrium rather than the decidua.
- Increta: When the chorionic villi penetrate the myometrium.
- Percreta: Occurs when it extends into the uterine serosa or adjacent organs.
- Previa: Occurs when it covers partially or completely the opening of the uterus better known as “internal os” AKA (the exit of the birth canal).
Placenta Previa.
When the placenta completely or partially covers the internal cervical os of the uterus, this condition is known as placenta previa.
- Placenta previa is classified as low-lying when it is within two centimeters of the cervical os but does not cover it.
- Partial previa when only a section of the internal os is covered by the placenta.
- Previa marginal when the edge of the placenta extends to the edge of the cervical os.
- Complete previa is when the internal is us covered completely by the placenta.
Risk Factors:
- Previous C-section delivery.
- History of previous abortions.
- History of previous intrauterine surgery.
- Smoking or doing drugs during pregnancy.
- A TWIN pregnancy.
- An increase in the number of births.
- Advanced maternal age.
Other articles you might want to read after:
Everything about the placenta. Ultrasound included.
Kick Counts During Pregnancy. How to do it and Why is Important.
Real Contractions vs Braxton Hicks. How to Know the Difference.
How does it look on ultrasound?
Placenta previa is easily diagnosed through ultrasound during pregnancy.
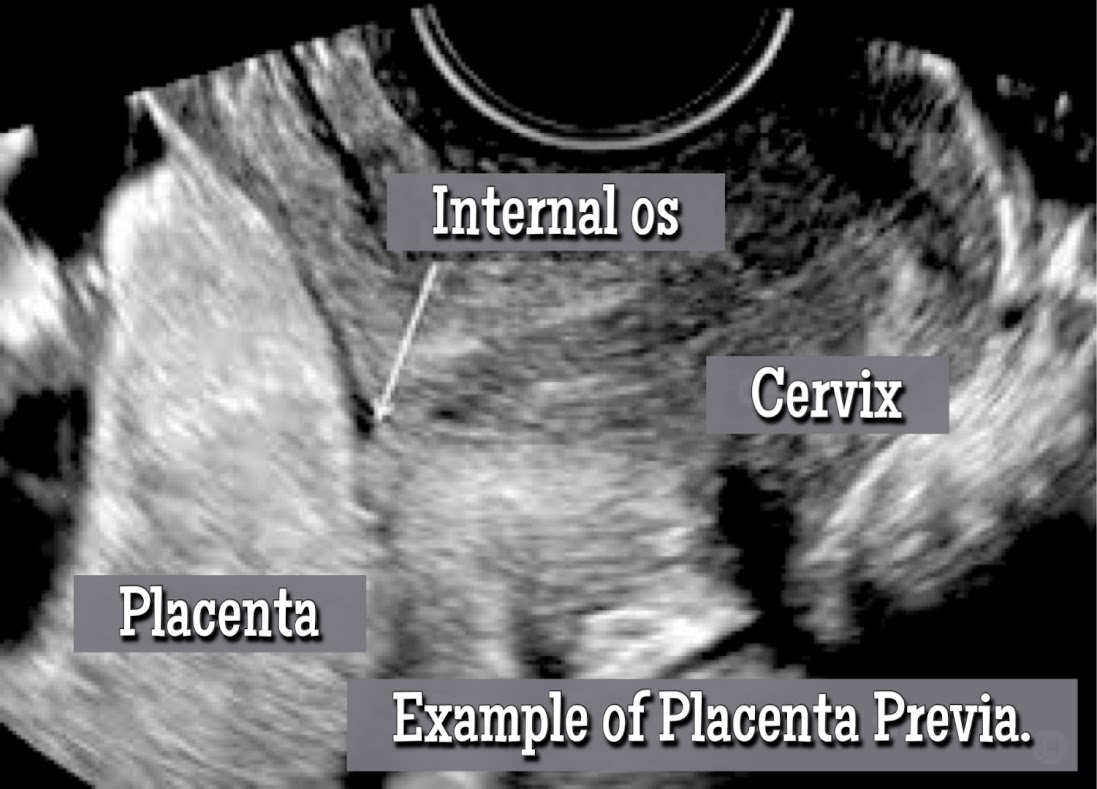
How does placenta previa affects a pregnancy?
What signs and symptoms are associated with this condition?
- Experiencing bright red bleeding from the vaginal area. It is common for the bleeding to begin anywhere in the second half of the pregnancy. It is also possible for it to be inconsistent as well, meaning that you might experience intermittent bleeding that comes and goes.
- Mild cramping or contractions in the abdominal region, which can also be felt in the tummy or back.
What are some of the potential issues that can arise from placenta previa?
For the mother:
Bleeding: Severe bleeding can happen at any point throughout pregnancy, including during labor and delivery. Blood loss can cause a number of negative side effects, including anemia, low blood pressure, pale complexion, and shortness of breath.
Early birth: Your healthcare professional may opt to perform an emergency cesarean section before your baby has reached full term if you are experiencing significant bleeding.
To the unborn child:
Birth too soon: If your bleeding is severe and you require an emergency C-section, then it is possible that your baby will be born before due date.
Low birth weight: Difficulty in maintaining a comfortable body temperature and slow weight gain are both potential adverse effects of having a low birth weight. Problems with breathing could arise from underdeveloped lungs, which can make breathing more challenging.
What treatment is there for placenta previa?
The objective is to bring you as close to the due date as is humanly possible. If bleeding does not stop, a cesarean section delivery is frequently the safest option. The treatment depends on the following:
- How much blood you’re losing right now.
- How far is your pregnancy.
- The position of both the placenta and your baby at the time of delivery.
- The wellbeing of both you and your unborn child.
If your healthcare professional discovers placenta previa early in the second trimester of your pregnancy, the condition may improve on its own. As your uterus grows to support your growing baby, the position of the placenta can shift therefore resolve. If your healthcare professional makes the diagnosis of the issue later in your pregnancy, you typically have a lower chance of having the placenta migrate to a higher position in your uterus.
If you are not experiencing any bleeding and your placenta is located close to or partially covering the cervix, your healthcare professional may propose the following:
- Lowering the intensity of vigorous activities such as running, lifting weights, and exercising or bed rest.
- There has to be no sexual contact, use of tampons, or douching.
- Appointments for prenatal care and ultrasounds should be held more frequently to monitor the well-being of the baby.
Other treatments could include the following for moderate to severe cases of placenta previa or for cases of persistent bleeding:
- The doctor ordered bed rest in the hospital.
- Medicine to stop labor from beginning too soon.
- Injections of steroids to speed up the maturation of the baby’s lungs.
- Transfusions of blood in the event that you encounter significant bleeding.
- In response to significant and uncontrollable bleeding, an emergency cesarean section will be done.
Final thoughts about today’s topic:
There is nothing that can be done to avoid having a placenta that is in the wrong position, and neither surgery nor medical treatment can correct it. You can reduce your risks by avoiding specific factors, including smoking and cocaine use, for example. It is extremely unusual for placenta previa to result in birth abnormalities. Your healthcare professional may recommend that you give birth earlier than expected if they believe that this is the most prudent moment to do. If you become pregnant again, there is a possibility that you could develop placenta previa once more. Keep in mind that you should always consult your physician if you have any questions. I hope that this article was helpful.
Zadi, xo
Disclaimer: The medical information on this post is for educational and entertainment use only. Under no circumstances, this information is to replace your doctor’s advice or to treat any disease. For proper care, always visit your doctor.


![[mailpoet_form id="2"]](https://ultrasoundfeminsider.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/IMG_3340-280x215.jpg)






